Involvement of H2O2 in superoxide-dismutase-induced enhancement of endothelium-dependent relaxation in rabbit mesenteric resistance artery
- PMID: 12770950
- PMCID: PMC1573853
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705255
Involvement of H2O2 in superoxide-dismutase-induced enhancement of endothelium-dependent relaxation in rabbit mesenteric resistance artery
Abstract
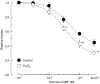
1 The mechanism underlying the enhancement by superoxide dismutase (SOD) of endothelium-dependent relaxation was investigated in rabbit mesenteric resistance arteries. 2 SOD (200 U ml(-1)) increased the production of H(2)O(2) in smooth muscle cells (as indicated by the use of an H(2)O(2)-sensitive fluorescent dye). 3 Neither SOD nor catalase (400 U ml(-1)) modified either the resting membrane potential or the hyperpolarization induced by acetylcholine (ACh, 1 micro M) in smooth muscle cells. 4 In arteries constricted with noradrenaline, the endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by ACh (0.01-1 micro M) was enhanced by SOD (200 U ml(-1)) (P<0.01). This action of SOD was inhibited by L-N(G)-nitroarginine (nitric oxide (NO)-synthase inhibitor) but not by either charybdotoxin+apamin (Ca(2+)-activated-K(+)-channel blockers) or diclofenac (cyclooxygenase inhibitor). 5 Neither ascorbate (50 micro M) nor tiron (0.3 mM), superoxide scavengers, had any effect on the ACh-induced relaxation, but each attenuated the enhancing effect of SOD on the ACh-induced relaxation. Similarly, catalase (400 U ml(-1)) inhibited the effect of SOD without changing the ACh-induced relaxation. 6 In endothelium-denuded strips constricted with noradrenaline, SOD enhanced the relaxation induced by the NO donor 1-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-(N-methyl-3-aminopropyl)-3-methyl-1-triazene (NOC-7) (P<0.05). Ascorbate and catalase each attenuated this effect of SOD. 7 H(2)O(2) (1 micro M) enhanced the relaxation on the noradrenaline contraction induced by NOC-7 and that induced by 8-bromo-cGMP, a membrane-permeable analogue of guanosine 3',5' cyclic monophosphate (cGMP). 8 SOD had no effect on cGMP production, whether measured in endothelium-intact strips following an application of ACh (0.1 micro M) or in endothelium-denuded strips following an application of NOC-7 (0.1 micro M). 9 It is suggested that in rabbit mesenteric resistance arteries, SOD increases the ACh-induced, endothelium-dependent relaxation by enhancing the action of NO in the smooth muscle via its H(2)O(2)-producing action (rather than via a superoxide-scavenging action).
Figures


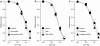
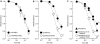
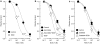
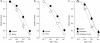

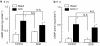
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II-induced modulation of endothelium-dependent relaxation in rabbit mesenteric resistance arteries.J Physiol. 2003 May 1;548(Pt 3):893-906. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.034116. Epub 2003 Mar 21. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12651915 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of attenuated endothelium-dependent relaxation seen in rabbit intrapulmonary vein following chronic nitroglycerine administration.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 May;145(2):193-202. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706178. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15753949 Free PMC article.
-
NO/PGI2-independent vasorelaxation and the cytochrome P450 pathway in rabbit carotid artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Feb;120(4):695-701. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0700945. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9051310 Free PMC article.
-
Pranidipine, a 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker that enhances nitric oxide-induced vascular relaxation.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2001 Spring;19(1):1-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2001.tb00179.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2001. PMID: 11314598 Review.
-
[Mechanisms underlying enhanced vasodilator responses to various vasodilator agents following endothelium removal in rat mesenteric resistance arteries].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007 Apr;127(4):729-33. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.127.729. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17409704 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Endothelium-dependent smooth muscle hyperpolarization: do gap junctions provide a unifying hypothesis?Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Mar;141(6):881-903. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705698. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15028638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of a common human gene variant of extracellular superoxide dismutase on endothelial function after endotoxin in mice.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 15;584(Pt 2):583-90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.140830. Epub 2007 Aug 23. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17717013 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of ACh-induced hyperpolarization and relaxation in rabbit jugular vein.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct;167(3):682-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02038.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22595036 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of bradykinin-induced relaxation of endothelin-1 and phenylephrine contractions of rat aorta by antioxidants.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Oct;28(10):1566-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00631.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007. PMID: 17883941 Free PMC article.
-
Catalase has negligible inhibitory effects on endothelium-dependent relaxations in mouse isolated aorta and small mesenteric artery.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Dec;140(7):1193-200. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705549. Epub 2003 Nov 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14597598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ABRAHAMSSON T., BRANDT U., MARKLUND S.L., SJOQVIST P.O. Vascular bound recombinant extracellular superoxide dismutase type C protects against the detrimental effects of superoxide radicals on endothelium-dependent arterial relaxation. Circ. Res. 1992;70:264–271. - PubMed
-
- BARLOW R.S., ABDALLA M.E., RICHARD E.W. H2O2 opens BKCa channels via the PLA2-arachidonic acid signaling cascade in coronary artery smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 2000;279:H475–H483. - PubMed
-
- BARLOW R.S., WHITE R.E. Hydrogen peroxide relaxes porcine coronary arteries by stimulating BKCa channel activity. Am. J. Physiol. 1998;275:H1283–H1289. - PubMed
-
- BHARADWAJ L., PRASAD K. Mediation of H2O2-induced vascular relaxation by endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1995;149–150:267–270. - PubMed
-
- DAEMEN M.J., LOMBARDI D.M., BOSMAN F.T., SCHWARTZ S.M. Angiotensin II induces smooth muscle cell proliferation in the normal and injured rat arterial wall. Circ. Res. 1991;68:450–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

