Epiretinal membrane removal in diabetic eyes: comparison of viscodissection with conventional methods of membrane peeling
- PMID: 12770972
- PMCID: PMC1771714
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.87.6.737
Epiretinal membrane removal in diabetic eyes: comparison of viscodissection with conventional methods of membrane peeling
Abstract
Aims: To compare conventional methods of epiretinal membrane peeling with viscodissection.
Methods: 154 eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) that underwent pars plana vitrectomy with membrane dissection (89 traditional, 65 viscodissection) were studied retrospectively. Incidence of retinal breaks (RBs), length of time under anaesthesia, postoperative intraocular pressure, retinal reattachment rate, and final visual acuity (VA) were measured.
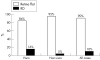
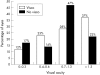
Results: To compare cases of similar complexity, a "complexity score" was defined. The average complexity score for cases done with and without viscodissection was 4.7 and 3.2, respectively. The mean frequency of RBs in eyes undergoing viscodissection was 0.43 (SD 0.5) v 0.14 (0.35) RBs/eye without viscodissection. In complex cases, the frequency of posterior/peripheral RBs was 0.31 (0.47)/0.13 (0.34) RBs/eye, respectively, with viscodissection v 0.12 (0.33)/0.23 (0.43) RBs/eye without viscodissection. None of these differences were statistically significant. The average preoperative/postoperative VA (logMAR) in the viscodissection cohort was 1.7/1.3 (range 0.3 to >1.9/0.1 to >1.9) v 1.4/1 (range 0.48 to >1.9/0.1 to >1.9) in the non-viscodissection cohort, among eyes with 6 months of follow up. Anaesthesia duration was significantly shorter for cases done without viscodissection (p=0.03), but cases done with viscodissection were significantly more complex than cases done without viscodissection (p<0.0001).
Conclusion: Viscodissection appears to be a safe and effective alternative technique in eyes with PDR. Owing to the retrospective nature of the study, additional studies are warranted.
Figures
Comment in
-
Viscosurgery in diabetic vitrectomy.Br J Ophthalmol. 2004 Apr;88(4):598-9. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004. PMID: 15031199 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stenkula S, Ivert L, Berglin L, et al. Healon Yellow as a surgical tool in maneuvering intraocular tissues. Ophthalmic Surg 1992;23:708–10. - PubMed
-
- Stenkula S, Ivert L, Gislason I, et al. The use of sodium-hyaluronate (Healon) in the treatment of retinal detachment. Ophthalmic Surg 1981;12:435–7. - PubMed
-
- Michels RG. Vitrectomy for complications of diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 1978;96:237–46. - PubMed
-
- Crafoord S, Stenkula S. Healon GV in posterior segment surgery. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1993;71:560–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
