Dishevelled activates Ca2+ flux, PKC, and CamKII in vertebrate embryos
- PMID: 12771126
- PMCID: PMC2199364
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200211094
Dishevelled activates Ca2+ flux, PKC, and CamKII in vertebrate embryos
Abstract
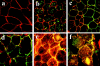
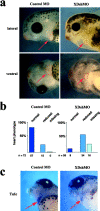
Wnt ligands and Frizzled (Fz) receptors have been shown to activate multiple intracellular signaling pathways. Activation of the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway has been described in greatest detail, but it has been reported that Wnts and Fzs also activate vertebrate planar cell polarity (PCP) and Wnt-Ca2+ pathways. Although the intracellular protein Dishevelled (Dsh) plays a dual role in both the Wnt-beta-catenin and the PCP pathways, its potential involvement in the Wnt-Ca2+ pathway has not been investigated. Here we show that a Dsh deletion construct, XDshDeltaDIX, which is sufficient for activation of the PCP pathway, is also sufficient for activation of three effectors of the Wnt-Ca2+ pathway: Ca2+ flux, PKC, and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CamKII). Furthermore, we find that interfering with endogenous Dsh function reduces the activation of PKC by Xfz7 and interferes with normal heart development. These data suggest that the Wnt-Ca2+ pathway utilizes Dsh, thereby implicating Dsh as a component of all reported Fz signaling pathways.
Figures




References
-
- Adler, P.N., and H. Lee. 2001. Frizzled signaling and cell-cell interactions in planar polarity. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13:635–640. - PubMed
-
- Boutros, M., and M. Mlodzik. 1999. Dishevelled: at the crossroads of divergent intracellular signaling pathways. Mech. Dev. 83:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Boutros, M., N. Paricio, D.I. Strutt, and M. Mlodzik. 1998. Dishevelled activates JNK and discriminates between JNK pathways in planar polarity and wingless signaling. Cell. 94:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Brown, J.D., S.E. Hallagan, L.L. McGrew, J.R. Miller, and R.T. Moon. 2000. The maternal Xenopus β-catenin signaling pathway, activated by frizzled homologs, induces goosecoid in a cell non-autonomous manner. Dev. Growth Differ. 42:347–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

