Contact inhibition of VEGF-induced proliferation requires vascular endothelial cadherin, beta-catenin, and the phosphatase DEP-1/CD148
- PMID: 12771128
- PMCID: PMC2199373
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200209019
Contact inhibition of VEGF-induced proliferation requires vascular endothelial cadherin, beta-catenin, and the phosphatase DEP-1/CD148
Abstract
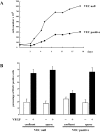
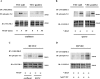
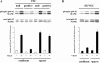
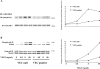
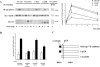
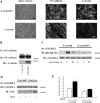
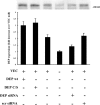
Confluent endothelial cells respond poorly to the proliferative signals of VEGF. Comparing isogenic endothelial cells differing for vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin) expression only, we found that the presence of this protein attenuates VEGF-induced VEGF receptor (VEGFR) 2 phosphorylation in tyrosine, p44/p42 MAP kinase phosphorylation, and cell proliferation. VE-cadherin truncated in beta-catenin but not p120 binding domain is unable to associate with VEGFR-2 and to induce its inactivation. beta-Catenin-null endothelial cells are not contact inhibited by VE-cadherin and are still responsive to VEGF, indicating that this protein is required to restrain growth factor signaling. A dominant-negative mutant of high cell density-enhanced PTP 1 (DEP-1)//CD148 as well as reduction of its expression by RNA interference partially restore VEGFR-2 phosphorylation and MAP kinase activation. Overall the data indicate that VE-cadherin-beta-catenin complex participates in contact inhibition of VEGF signaling. Upon stimulation with VEGF, VEGFR-2 associates with the complex and concentrates at cell-cell contacts, where it may be inactivated by junctional phosphatases such as DEP-1. In sparse cells or in VE-cadherin-null cells, this phenomenon cannot occur and the receptor is fully activated by the growth factor.
Figures
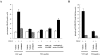
References
-
- Balconi, G., R. Spagnuolo, and E. Dejana. 2000. Development of endothelial cell lines from embryonic stem cells: a tool for studying genetically manipulated endothelial cells in vitro. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20:1443–1451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

