The phage T4 restriction endoribonuclease RegB: a cyclizing enzyme that requires two histidines to be fully active
- PMID: 12771201
- PMCID: PMC156712
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg377
The phage T4 restriction endoribonuclease RegB: a cyclizing enzyme that requires two histidines to be fully active
Abstract
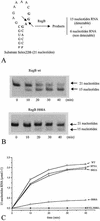
The regB gene, from the bacteriophage T4, codes for an endoribonuclease that controls the expression of a number of phage early genes. The RegB protein cleaves its mRNA substrates with an almost absolute specificity in the middle of the tertranucleotide GGAG, making it a unique well-defined restriction endoribonuclease. This striking protein has no homology to any known RNase and its catalytic mechanism has never been investigated. Here, we show, using 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), that RegB produces a cyclic 2',3'-phosphodiester product. In order to determine the residues crucial for its activity, we prepared all the histidine-to- alanine point mutants of RegB. The activity of these mutants was characterized both in vivo and in vitro. In addition, their binding capability was quantified by surface plasmon resonance and their structural integrity was probed by 1H/15N NMR correlation spectroscopy. The results obtained show that only the H48A and the H68A substitutions significantly reduce RegB activity without changing its ability to bind the substrate or affecting its overall structure. Altogether, our results define RegB as a new cyclizing RNase and present His48 and His68 as potent catalytic residues. The effect of the in vivo selected R52L mutation is also described and discussed.
Figures
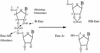


Similar articles
-
First structural investigation of the restriction ribonuclease RegB: NMR spectroscopic conditions, 13C/15N double-isotopic labelling and two-dimensional heteronuclear spectra.Protein Expr Purif. 2004 Mar;34(1):158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2003.11.002. Protein Expr Purif. 2004. PMID: 14766312
-
The sequences and activities of RegB endoribonucleases of T4-related bacteriophages.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Oct 14;32(18):5582-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh892. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15486207 Free PMC article.
-
1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignment of phage T4 endoribonuclease RegB.Biomol NMR Assign. 2007 Jul;1(1):73-4. doi: 10.1007/s12104-007-9021-4. Epub 2007 Jul 4. Biomol NMR Assign. 2007. PMID: 19636830
-
Post-transcriptional controls in bacteriophage T4: roles of the sequence-specific endoribonuclease RegB.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1995 Aug;17(1-2):141-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1995.tb00196.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1995. PMID: 7669340 Review.
-
Nucleotide binding architecture for secreted cytotoxic endoribonucleases.Biochimie. 2013 Jun;95(6):1087-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.12.015. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 23274129 Review.
Cited by
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of Nsp15 from SARS coronavirus.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2006 Apr 1;62(Pt 4):409-11. doi: 10.1107/S1744309106009407. Epub 2006 Mar 25. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2006. PMID: 16582498 Free PMC article.
-
A novel family of sequence-specific endoribonucleases associated with the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 18;283(29):20361-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803225200. Epub 2008 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18482976 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and characterization of DNA libraries from cultured phages and environmental viromes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Oct 23;90(10):e0117124. doi: 10.1128/aem.01171-24. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39315792 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of RegB endoribonuclease by S1 ribosomal protein requires an 11 nt conserved sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(22):6549-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl911. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 17130171 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and initial characterization of YloC, a novel endoribonuclease in Bacillus subtilis.RNA. 2022 Feb;28(2):227-238. doi: 10.1261/rna.078962.121. Epub 2021 Nov 23. RNA. 2022. PMID: 34815358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanson B., Hu,R.M., Troitskaya,E., Mathy,N. and Uzan,M. (2000) Endoribonuclease RegB from bacteriophage T4 is necessary for the degradation of early but not middle or late mRNAs. J. Mol. Biol., 297, 1063–1074. - PubMed
-
- Lebars I., Hu,R.M., Lallemand,J.Y., Uzan,M. and Bontems,F. (2001) Role of the substrate conformation and of the S1 protein in the cleavage efficiency of the T4 endoribonuclease RegB. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 13264–13272. - PubMed
-
- Ruckman J., Ringquist,S., Brody,E. and Gold,L. (1994) The bacteriophage T4 regB ribonuclease. Stimulation of the purified enzyme by ribosomal protein S1. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 26655–26662. - PubMed
-
- Lima W.F., Wu,H. and Crooke,S.T. (2001) Human RNases H. Methods Enzymol., 341, 430–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

