Domain mapping of Escherichia coli RecQ defines the roles of conserved N- and C-terminal regions in the RecQ family
- PMID: 12771204
- PMCID: PMC156711
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg376
Domain mapping of Escherichia coli RecQ defines the roles of conserved N- and C-terminal regions in the RecQ family
Abstract
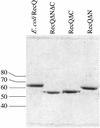
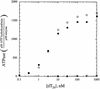
RecQ DNA helicases function in DNA replication, recombination and repair. Although the precise cellular roles played by this family of enzymes remain elusive, the importance of RecQ proteins is clear; mutations in any of three human RecQ genes lead to genomic instability and cancer. In this report, proteolysis is used to define a two-domain structure for Escherichia coli RecQ, revealing a large (approximately 59 kDa) N-terminal and a small (approximately 9 kDa) C-terminal domain. A short N-terminal segment (7 or 21 residues) is also shown to be sensitive to proteases. The effects of removing these regions of RecQ are tested in vitro. Removing 21 N-terminal residues from RecQ severely diminishes its DNA-dependent ATPase and helicase activities, but does not affect its ability to bind DNA in electrophoretic mobility shift assays. In contrast, removing the approximately 9 kDa C-terminal domain from RecQ results in a fragment with normal levels of ATPase and helicase activity, but that has lost the ability to stably associate with DNA. These results establish the biochemical roles of an N-terminal sequence motif in RecQ catalytic function and for the C-terminal RecQ domain in stable DNA binding.
Figures
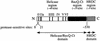

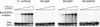

Similar articles
-
Characterization and mutational analysis of the RecQ core of the bloom syndrome protein.J Mol Biol. 2003 Jun 27;330(1):29-42. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00534-5. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12818200
-
A conserved G4 DNA binding domain in RecQ family helicases.J Mol Biol. 2006 May 12;358(4):1071-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.077. Epub 2006 Feb 7. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16530788
-
Coupling DNA-binding and ATP hydrolysis in Escherichia coli RecQ: role of a highly conserved aromatic-rich sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Dec 9;33(22):6982-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki999. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16340008 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of RecQ DNA helicases.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Mar-Apr;39(2):79-97. doi: 10.1080/10409230490460756. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15217989 Review.
-
RecQ family helicases: roles as tumor suppressor proteins.Oncogene. 2002 Dec 16;21(58):9008-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205959. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12483516 Review.
Cited by
-
The N-terminal region of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe RecQ helicase, Rqh1p, physically interacts with Topoisomerase III and is required for Rqh1p function.Mol Genet Genomics. 2005 Mar;273(1):102-14. doi: 10.1007/s00438-005-1111-3. Epub 2005 Feb 9. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005. PMID: 15702347
-
RecQ Helicase Somatic Alterations in Cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 15;9:887758. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.887758. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35782872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole genome sequence of the Treponema pallidum subsp. endemicum strain Bosnia A: the genome is related to yaws treponemes but contains few loci similar to syphilis treponemes.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Nov 6;8(11):e3261. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003261. eCollection 2014. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 25375929 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of human RECQL5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae causes transcription defects and transcription-associated genome instability.Mol Genet Genomics. 2024 May 26;299(1):59. doi: 10.1007/s00438-024-02152-3. Mol Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38796829 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the SSB binding site on E. coli RecQ reveals a conserved surface for binding SSB's C terminus.J Mol Biol. 2009 Feb 27;386(3):612-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.12.065. Epub 2009 Jan 3. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19150358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frei C. and Gasser,S.M. (2000) RecQ-like helicases: the DNA replication checkpoint connection. J. Cell Sci., 113 (Pt 15), 2641–2646. - PubMed
-
- Karow J.K., Wu,L. and Hickson,I.D. (2000) RecQ family helicases: roles in cancer and aging. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 10, 32–38. - PubMed
-
- Nakayama H., Nakayama,K., Nakayama,R., Irino,N., Nakayama,Y. and Hanawalt,P.C. (1984) Isolation and genetic characterization of a thymineless death-resistant mutant of Escherichia coli K12: identification of a new mutation (recQ1) that blocks the RecF recombination pathway. Mol. Gen. Genet., 195, 474–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

