The Drosophila Corto protein interacts with Polycomb-group proteins and the GAGA factor
- PMID: 12771214
- PMCID: PMC156716
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg381
The Drosophila Corto protein interacts with Polycomb-group proteins and the GAGA factor
Abstract
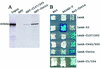
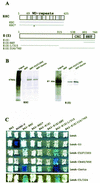
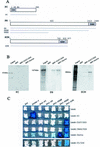
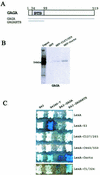
In Drosophila, PcG complexes provide heritable transcriptional silencing of target genes. Among them, the ESC/E(Z) complex is thought to play a role in the initiation of silencing whereas other complexes such as the PRC1 complex are thought to maintain it. PcG complexes are thought to be recruited to DNA through interaction with DNA binding proteins such as the GAGA factor, but no direct interactions between the constituents of PcG complexes and the GAGA factor have been reported so far. The Drosophila corto gene interacts with E(z) as well as with genes encoding members of maintenance complexes, suggesting that it could play a role in the transition between the initiation and maintenance of PcG silencing. Moreover, corto also interacts genetically with Trl, which encodes the GAGA factor, suggesting that it may serve as a mediator in recruiting PcG complexes. Here, we show that Corto bears a chromo domain and we provide evidence for in vivo association of Corto with ESC and with PC in embryos. Moreover, we show by GST pull-down and two-hybrid experiments that Corto binds to E(Z), ESC, PH, SCM and GAGA and co-localizes with these proteins on a few sites on polytene chromosomes. These results reinforce the idea that Corto plays a role in PcG silencing, perhaps by confering target specificity.
Figures


References
-
- Lewis E.B. (1978) A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature, 276, 565–570. - PubMed
-
- McKeon J., Slade,E., Sinclair,D.A., Cheng,N., Couling,M. and Brock,H.W. (1994) Mutations in some Polycomb group genes of Drosophila interfere with regulation of segmentation genes. Mol. Gen. Genet., 244, 474–483. - PubMed
-
- Daubresse G., Deuring,R., Moore,L., Papoulas,O., Zakrajsek,I., Waldrip,W.R., Scott,M.P., Kennison,J.A. and Tamkun,J.W. (1999) The Drosophila kismet gene is related to chromatin-remodeling factors and is required for both segmentation and segment identity. Development, 126, 1175–1187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

