NF-kappaB and virus infection: who controls whom
- PMID: 12773372
- PMCID: PMC156764
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg267
NF-kappaB and virus infection: who controls whom
Abstract
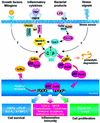
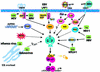
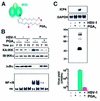
Among the different definitions of viruses, 'pirates of the cell' is one of the most picturesque, but also one of the most appropriate. Viruses have been known for a long time to utilize a variety of strategies to penetrate cells and, once inside, to take over the host nucleic acid and protein synthesis machinery to build up their own components and produce large amounts of viral progeny. As their genomes carry a minimal amount of information, encoding only a few structural and regulatory proteins, viruses are largely dependent on their hosts for survival; however, despite their apparent simplicity, viruses have evolved different replicative strategies that are regulated in a sophisticated manner. During the last years, the study of the elaborate relationship between viruses and their hosts has led to the understanding of how viral pathogens not only are able to alter the host metabolism via their signaling proteins, but are also able to hijack cellular signaling pathways and transcription factors, and control them to their own advantage. In particular, the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway appears to be an attractive target for common human viral pathogens. This review summarizes what is known about the control of NF-kappaB by viruses, and discusses the possible outcome of NF-kappaB activation during viral infection, which may benefit either the host or the pathogen.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NF-κB as a potential therapeutic target in microbial diseases.Mol Biosyst. 2012 Apr;8(4):1108-20. doi: 10.1039/c2mb05335g. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Mol Biosyst. 2012. PMID: 22311336 Review.
-
[Influenza viruses and intracellular signalling pathways].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2006 Mar-Apr;119(3-4):101-11. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2006. PMID: 16573200 Review. German.
-
Viral interference with innate immunity by preventing NF-κB activity.Cell Microbiol. 2012 Feb;14(2):168-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01720.x. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22050732 Review.
-
Viral strategies in modulation of NF-kappaB activity.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2003;51(6):367-75. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2003. PMID: 14692658 Review.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Korean Propolis on Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Mucosal Injury Mice Model.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 3;14(21):4644. doi: 10.3390/nu14214644. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364906 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2, HIV, and HPV: Convergent evolution of selective regulation of cGAS-STING signaling.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28220. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28220. Epub 2022 Oct 26. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36229923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bat Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Like Coronavirus WIV1 Encodes an Extra Accessory Protein, ORFX, Involved in Modulation of the Host Immune Response.J Virol. 2016 Jun 24;90(14):6573-6582. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03079-15. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27170748 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Variability across Human Populations: A Focus on DNA Methylation Profiles of the KRTCAP3, MAD1L1 and BRSK2 Genes.Genome Biol Evol. 2016 Sep 19;8(9):2760-73. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw186. Genome Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27503294 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine arterivirus activates the NF-kappaB pathway through IkappaB degradation.Virology. 2005 Nov 10;342(1):47-59. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.07.034. Epub 2005 Aug 29. Virology. 2005. PMID: 16129468 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amici C., Belardo,G., Rossi,A. and Santoro,M.G. (2001) Activation of IκB kinase by herpes simplex virus type 1. A novel target for anti-herpetic therapy. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 28759–28766. - PubMed
-
- Baud V. and Karin,M. (2001) Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol., 11, 372–377. - PubMed
-
- Biswas D.K. et al. (1998) Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by combination of a novel inhibitor of TNF-α with AZT. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol., 15, 426–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

