The role of Ppe1/PP6 phosphatase for equal chromosome segregation in fission yeast kinetochore
- PMID: 12773390
- PMCID: PMC156763
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg266
The role of Ppe1/PP6 phosphatase for equal chromosome segregation in fission yeast kinetochore
Abstract
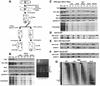
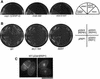
Mis12 is a kinetochore protein essential for equal chromosome segregation and is evolutionarily conserved from yeast to human. In this study, we report the isolation and characterization of suppressors of the mis12 mutant in fission yeast. Our results indicate that Mis12 is negatively regulated by a highly conserved protein phosphatase Ppe1 (scSit4/dmPPV/hPP6) or its bound partner Ekc1 (scSAP), and it is positively regulated by a counteracting kinase Gsk3. Mass spectrometry analysis shows that at least two sites in Mis12 are phosphorylated. This mechanism of suppression occurs at the level of localization recovery of Mis12 to the kinetochore chromatin. Consistently, Mis12 and a subpopulation of Ppe1/Ekc1 were found to behave like non-histone-type chromatin-associating proteins in the chromatin fractionation assay. Mutant analysis of Ppe1 and Ekc1 revealed that they are important for faithful chromosome segregation, as the mutants exhibited unequal chromosome segregation similar to mis12 in the presence of a low concentration of tubulin poison. Ppe1/PP6 directly or indirectly modulates kinetochore chromatin protein Mis12 to ensure progression into normal anaphase.
Figures





References
-
- Bastians H. and Ponstingl,H. (1996) The novel human protein serine/threonine phosphatase 6 is a functional homologue of budding yeast Sit4p and fission yeast ppe1, which are involved in cell cycle regulation. J. Cell Sci., 109, 2865–2874. - PubMed
-
- Beck T. and Hall,M.N. (1999) The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature, 402, 689–692. - PubMed
-
- Cohen P.T. (1997) Novel protein serine/threonine phosphatases: variety is the spice of life. Trends Biochem. Sci., 22, 245–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

