Synergism between calcium and cyclic GMP in cyclic AMP response element-dependent transcriptional regulation requires cooperation between CREB and C/EBP-beta
- PMID: 12773552
- PMCID: PMC156132
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4066-4082.2003
Synergism between calcium and cyclic GMP in cyclic AMP response element-dependent transcriptional regulation requires cooperation between CREB and C/EBP-beta
Abstract
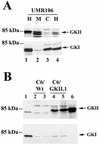
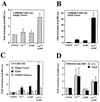
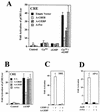
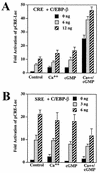
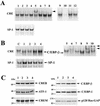
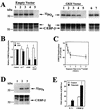
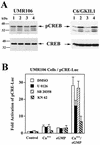
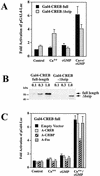
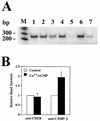
Calcium induces transcriptional activation of the fos promoter by activation of the cyclic AMP response element (CRE)-binding protein (CREB), and in some cells its effect is enhanced synergistically by cyclic GMP (cGMP) through an unknown mechanism. We observed calcium-cGMP synergism in neuronal and osteogenic cells which express type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase (G-kinase); the effect on the fos promoter was mediated by the CRE and proportional to G-kinase activity. Dominant negative transcription factors showed involvement of CREB- and C/EBP-related proteins but not of AP-1. Expression of C/EBP-beta but not C/EBP-alpha or -delta enhanced the effects of calcium and cGMP on a CRE-dependent reporter gene. The transactivation potential of full-length CREB fused to the DNA-binding domain of Gal4 was increased synergistically by calcium and cGMP, and overexpression of C/EBP-beta enhanced the effect, while a dominant negative C/EBP inhibited it. With a mammalian two-hybrid system, coimmunoprecipitation experiments, and in vitro binding studies, we demonstrated that C/EBP-beta and CREB interacted directly; this interaction involved the C terminus of C/EBP-beta but occurred independently of CREB's leucine zipper domain. CREB Ser(133) phosphorylation was stimulated by calcium but not by cGMP; in cGMP-treated cells, (32)PO(4) incorporation into C/EBP-beta was decreased and C/EBP-beta/CRE complexes were increased, suggesting regulation of C/EBP-beta functions by G-kinase-dependent dephosphorylation. C/EBP-beta and CREB associated with the fos promoter in intact cells, and the amount of promoter-associated C/EBP-beta was increased by calcium and cGMP. We conclude that calcium and cGMP transcriptional synergism requires cooperation of CREB and C/EBP-beta, with calcium and cGMP modulating the phosphorylation states of CREB and C/EBP-beta, respectively.
Figures

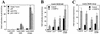

References
-
- Aguirre, J., L. Buttery, M. O'Shaughnessy, F. Afzal, I. F. de Marticorena, M. Hukkanen, P. Huang, I. Maclntyre, and J. Polak. 2001. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene-deficient mice demonstrate marked retardation in postnatal bone formation, reduced bone volume, and defects in osteoblast maturation and activity. Am. J. Pathol. 158:247-257. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belsham, D. D., and P. L. Mellon. 2000. Transcription factors Oct-1 and C/EBPβ (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β) are involved in the glutamate/nitric oxide/cyclic-guanosine 5′-monophosphate-mediated repression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 14:212-228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
