Deacetylase activity is required for recruitment of the basal transcription machinery and transactivation by STAT5
- PMID: 12773560
- PMCID: PMC156147
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4162-4173.2003
Deacetylase activity is required for recruitment of the basal transcription machinery and transactivation by STAT5
Abstract
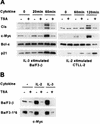
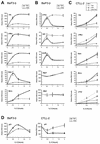
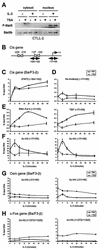
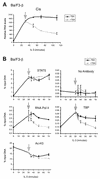
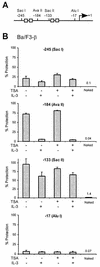
The signal transducer and activator of transcription STAT5 plays a major role in the cellular response to cytokines, but the mechanism by which it activates transcription remains poorly understood. We show here that deacetylase inhibitors (trichostatin A, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, and sodium butyrate) prevent induction of endogenous STAT5 target genes, implying that a deacetylase activity is required for that process. Microarray analyses revealed that this requirement is common to all STAT5 target genes. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we show that, following STAT5 DNA binding, deacetylase inhibitors block transcription initiation by preventing recruitment of the basal transcription machinery. This inhibition is not due to effects on histone H3 and H4 acetylation or chromatin remodeling within the promoter region. This novel mechanism of transactivation by STAT5 provides a rationale for the use of deacetylase inhibitors for therapeutic intervention in STAT5-associated cancers.
Figures
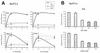
Similar articles
-
Chromatin acetylation and remodeling at the Cis promoter during STAT5-induced transcription.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Dec 1;31(23):6882-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg907. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 14627821 Free PMC article.
-
NCoA-1/SRC-1 is an essential coactivator of STAT5 that binds to the FDL motif in the alpha-helical region of the STAT5 transactivation domain.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 14;278(46):45340-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303644200. Epub 2003 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12954634
-
Functional interaction of STAT5 and nuclear receptor co-repressor SMRT: implications in negative regulation of STAT5-dependent transcription.EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6836-44. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6836. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11726519 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5).Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;36(11):2120-4. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2003.11.008. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15313458 Review.
-
Coactivators in gene regulation by STAT5.Vitam Horm. 2005;70:359-86. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(05)70012-1. Vitam Horm. 2005. PMID: 15727811 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary compounds as potent inhibitors of the signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) 3 regulatory network.Genes Nutr. 2012 Apr;7(2):111-25. doi: 10.1007/s12263-012-0281-y. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Genes Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22274779 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signalling and T-cell lymphomas.Immunology. 2005 Mar;114(3):301-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02091.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 15720432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inteferons pen the JAK-STAT pathway.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008 Aug;19(4):311-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.08.010. Epub 2008 Aug 26. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18765289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endotoxin- and mechanical stress-induced epigenetic changes in the regulation of the nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase promoter.Pulm Circ. 2016 Dec;6(4):539-544. doi: 10.1086/688761. Pulm Circ. 2016. PMID: 28090296 Free PMC article.
-
Investigational histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) in myeloproliferative neoplasms.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016 Dec;25(12):1393-1403. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2016.1250882. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27756180 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agalioti, T., S. Lomvardas, B. Parekh, J. Yie, T. Maniatis, and D. Thanos. 2000. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-β promoter. Cell 103:667-678. - PubMed
-
- Ahringer, J. 2000. NuRD and SIN3 histone deacetylase complexes in development. Trends Genet. 16:351-356. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S. L. 2002. Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12:142-148. - PubMed
-
- Brondello, J. M., A. Brunet, J. Pouyssegur, and F. R. McKenzie. 1997. The dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 and -2 are induced by the p42/p44MAPK cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 272:1368-1376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
