Methylation of histone H3 by Set2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is linked to transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 12773564
- PMCID: PMC427527
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4207-4218.2003
Methylation of histone H3 by Set2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is linked to transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II
Abstract
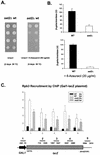
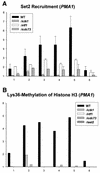
Set2 methylates Lys36 of histone H3. We show here that yeast Set2 copurifies with RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses demonstrated that Set2 and histone H3 Lys36 methylation are associated with the coding regions of several genes that were tested and correlate with active transcription. Both depend, as well, on the Paf1 elongation factor complex. The C terminus of Set2, which contains a WW domain, is also required for effective Lys36 methylation. Deletion of CTK1, encoding an RNAPII CTD kinase, prevents Lys36 methylation and Set2 recruitment, suggesting that methylation may be triggered by contact of the WW domain or C terminus of Set2 with Ser2-phosphorylated CTD. A set2 deletion results in slight sensitivity to 6-azauracil and much less beta-galactosidase produced by a reporter plasmid, resulting from a defect in transcription. In synthetic genetic array (SGA) analysis, synthetic growth defects were obtained when a set2 deletion was combined with deletions of all five components of the Paf1 complex, the chromodomain elongation factor Chd1, the putative elongation factor Soh1, the Bre1 or Lge1 components of the histone H2B ubiquitination complex, or the histone H2A variant Htz1. SET2 also interacts genetically with components of the Set1 and Set3 complexes, suggesting that Set1, Set2, and Set3 similarly affect transcription by RNAPII.
Figures



References
-
- Allen, C., N. A. Kent, H. S. Jones, J. O'Sullivan, A. Aranda, and N. J. Proudfoot. 2002. A role for chromatin remodeling in transcriptional termination by RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell 10:1442-1452. - PubMed
-
- Allison, L. A., M. Moyle, M. Shales, and C. J. Ingles. 1985. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell 42:599-610. - PubMed
-
- Bähler, J., J. Wu, M. S. Longtine, N. G. Shah, A. McKenzie III, A. B. Steever, A. Wach, P. Philippsen, and J. R. Pringle. 1998. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14:943-951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
