Effects of rho kinase and actin stress fibers on sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity and activation of G(1) phase cyclin-dependent kinases
- PMID: 12773570
- PMCID: PMC156148
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4283-4294.2003
Effects of rho kinase and actin stress fibers on sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity and activation of G(1) phase cyclin-dependent kinases
Retraction in
-
Effects of rho kinase and actin stress fibers on sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity and activation of G1 phase cyclin-dependent kinases.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;26(13):5203. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00844-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16782904 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
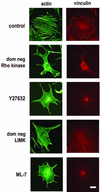
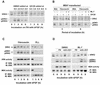
We recently reported that Rho kinase is required for sustained ERK signaling and the consequent mid-G(1) phase induction of cyclin D1 in fibroblasts. The results presented here indicate that these Rho kinase effects are mediated by the formation of stress fibers and the consequent clustering of alpha5beta1 integrin. Mechanistically, alpha5beta1 signaling and stress fiber formation allowed for the sustained activation of MEK, and this effect was mediated upstream of Ras-GTP loading. Interestingly, disruption of stress fibers with ML-7 led to G(1) phase arrest while comparable disruption of stress fibers with Y27632 (an inhibitor of Rho kinase) or dominant-negative Rho kinase led to a more rapid progression through G(1) phase. Inhibition of either MLCK or Rho kinase blocked sustained ERK signaling, but only Rho kinase inhibition allowed for the induction of cyclin D1 and activation of cdk4 via Rac/Cdc42. The levels of cyclin E, cdk2, and their major inhibitors, p21(cip1) and p27(kip1), were not affected by inhibition of MLCK or Rho kinase. Overall, our results indicate that Rho kinase-dependent stress fiber formation is required for sustained activation of the MEK/ERK pathway and the mid-G(1) phase induction of cyclin D1, but not for other aspects of cdk4 or cdk2 activation. They also emphasize that G(1) phase cell cycle progression in fibroblasts does not require stress fibers if Rac/Cdc42 signaling is allowed to induce cyclin D1.
Figures






Comment in
-
Findings of misconduct in science.NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2007 Jul 20:NOT-OD-07-075. NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2007. PMID: 17647301 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adnane, J., F. A. Bizouarn, Y. Qian, A. D. Hamilton, and S. M. Sebti. 1998. p21WAF1/CIP1 is upregulated by the geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitor GGTI-298 through a transforming growth factor beta- and Sp1-responsive element: involvement of the small GTPase RhoA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:6962-6970. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agnew, B. J., L. S. Minamide, and J. R. Bamburg. 1995. Reactivation of phosphorylated actin depolymerizing factor and identification of the regulatory site. J. Biol. Chem. 270:17582-17587. - PubMed
-
- Amano, M., K. Chihara, K. Kimura, Y. Fukata, N. Nakamura, Y. Matsuura, and K. Kaibuchi. 1997. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho kinase. Science 275:1308-1311. - PubMed
-
- Amano, M., M. Ito, K. Kimura, Y. Fukata, K. Chihara, T. Nakano, Y. Matsuura, and K. Kaibuchi. 1996. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho kinase). J. Biol. Chem. 271:20246-20249. - PubMed
-
- Aplin, A. E., S. M. Short, and R. L. Juliano. 1999. Anchorage-dependent regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by growth factors is supported by a variety of integrin α chains. J. Biol. Chem. 274:31223-31228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
