Effects of environmental enrichment on spatial memory and neurochemistry in middle-aged mice
- PMID: 12773583
- PMCID: PMC202309
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.50703
Effects of environmental enrichment on spatial memory and neurochemistry in middle-aged mice
Abstract
The present study compared the effects of environmental enrichment on spatial memory, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) activity, and synaptophysin levels in middle-aged male and female mice. Prior to testing, a subset of 18-month-old male and female C57BL/6 mice was housed with two to three toys and a running wheel in the home cage for up to 29 d. Adult mice (7 mo) of both sexes and the remaining middle-aged mice were group (social) housed, but not exposed to enriching objects. After the enrichment period, all mice were tested in a 1-day version of the Morris water maze, in which both spatial and nonspatial memory were assessed. Immediately after testing, the hippocampus and frontoparietal cortex were dissected, and GAD activity and synaptophysin levels were measured. Environmental enrichment reduced the age-related impairment in spatial acquisition and retention; relative to adult social controls, middle-aged enriched mice were unimpaired, whereas middle-aged social controls were impaired. This reduction was similar in middle-aged males and females. Enrichment did not affect cued memory in either sex. Although hippocampal GAD activity was increased by enrichment in males, all other neurochemical measurements were unaffected by enrichment or aging in either sex. These data suggest that environmental enrichment initiated at middle age can reduce age-related impairments in spatial memory in males and females, although the underlying neurobiological mechanisms of this effect remain unknown.
Figures
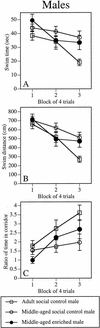


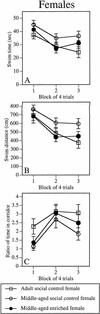

References
-
- Baxter, M.G., Lanthorn, T.H., Frick, K.M., Golski, S., Wan, R.-Q., and Olton, D.S. 1994a. D-cycloserine, a novel cognitive enhancer, improves spatial memory in aged rats. Neurobiol. Aging 15: 207–213. - PubMed
-
- Baxter, M.G., Rohrbach, K.W., Tam, W., Zaczek, R., Frick, K.M., Golski, S., Wan, R.-Q., and Olton, D.S. 1994b. Effects of linopirdine (DuP 996) and X9121 on age-related memory impairments and on the cholinergic system. Drug Dev. Res. 31: 186–196.
-
- Berger-Sweeney, J., Berger, U.V., Sharma, M., and Paul, C.A. 1994. Effects of carbon dioxide-induced anesthesia on cholinergic parameters in rat brain. Lab. Anim. Sci. 44: 369–371. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brown, R.T. 1968. Early experience and problem-solving ability. J. Comp. Physiol. Psych. 65: 433–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
