Mapping the genetic variation of executive attention onto brain activity
- PMID: 12773616
- PMCID: PMC165888
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0732088100
Mapping the genetic variation of executive attention onto brain activity
Abstract
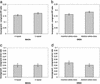
Brain imaging data have repeatedly shown that the anterior cingulate cortex is an important node in the brain network mediating conflict. We previously reported that polymorphisms in dopamine receptor (DRD4) and monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) genes showed significant associations with efficiency of handling conflict as measured by reaction time differences in the Attention Network Test (ANT). To examine whether this genetic variation might contribute to differences in brain activation within the anterior cingulate cortex, we genotyped 16 subjects for the DRD4 and MAOA genes who had been scanned during the ANT. In each of the two genes previously associated with more efficient handling of conflict in reaction time experiments, we found a polymorphism in which persons with the allele associated with better behavioral performance showed significantly more activation in the anterior cingulate while performing the ANT than those with the allele associated with worse performance. The results demonstrate how genetic differences among individuals can be linked to individual differences in neuromodulators and in the efficiency of the operation of an appropriate attentional network.
Figures

References
-
- Bush, G., Luu, P. & Posner, M. I. (2000) Trends Cognit. Sci. 4, 215-222. - PubMed
-
- Botvinick, M. M., Braver, T. S., Barch, D. M., Carter, C. S. & Cohen, J. D. (2001) Psychol. Rev. 108, 624-652. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald, A. W., Cohen, J. D., Stenger, V. A. & Carter, C. S. (2000) Science 288, 1835-1838. - PubMed
-
- Fan, J., Flombaum, J. I., McCandliss, B. D., Thomas, K. M. & Posner, M. I. (2003) NeuroImage 18, 42-57. - PubMed
-
- Fan, J., McCandliss, B. D., Flombaum, J. I. & Posner, M. I. (2001) in Society for Neuroscience 2001 Annual Meeting (Soc. Neurosci., San Diego), p. 215.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

