Differential risks of covarying and pure components in mother and teacher reports of externalizing and internalizing behavior across ages 5 to 14
- PMID: 12774860
- PMCID: PMC2764261
- DOI: 10.1023/a:1023277413027
Differential risks of covarying and pure components in mother and teacher reports of externalizing and internalizing behavior across ages 5 to 14
Abstract
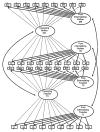
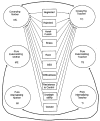
In a sample of 585 children assessed in kindergarten through 8th grade, we fit a confirmatory factor model to both mother- and teacher-reported symptoms on the Achenbach checklists (CBCL, TRF) and determined that a covariation factor of externalizing and internalizing behaviors existed, in addition to the pure-form factors of externalizing and internalizing for each reporter. In 3 structural equation models, between 8 and 67% of the variance in these 6 latent factors was accounted for by a set of antecedent child, sociocultural, parenting, and peer risk variables. Each of the 6 latent factors, taken 2 at a time, was predicted by a unique set of risk variables; however, there were some patterns that held for both mother- and teacher-report symptom factors: Child temperamental unadaptability and female gender were predictors of higher internalizing symptoms; child temperamental resistance to control, parental harsh punishment, male gender, low SES, and peer rejection were related to higher externalizing symptoms whereas child temperamental unadaptability was related to lower externalizing symptoms; and peer rejection and family stress were also related to the covarying, externalizing-plus-internalizing component of both mother and teacher reports.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of discrepancies between fathers and mothers in rating behaviors of preschool children with and without ADHD.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017 Mar;26(3):365-376. doi: 10.1007/s00787-016-0897-3. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27578230 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-domain growth analysis: externalizing and internalizing behaviors during 8 years of childhood.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2000 Apr;28(2):161-79. doi: 10.1023/a:1005122814723. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2000. PMID: 10834768 Free PMC article.
-
Role of temperament in early adolescent pure and co-occurring internalizing and externalizing problems using a bifactor model: Moderation by parenting and gender.Dev Psychopathol. 2016 Nov;28(4pt2):1487-1504. doi: 10.1017/S0954579415001224. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Dev Psychopathol. 2016. PMID: 26646352 Free PMC article.
-
Behaviors of children who are exposed and not exposed to intimate partner violence: an analysis of 330 black, white, and Hispanic children.Pediatrics. 2003 Sep;112(3 Pt 1):e202-7. doi: 10.1542/peds.112.3.e202. Pediatrics. 2003. PMID: 12949313
-
The impact of children's internalizing and externalizing problems on parenting: Transactional processes and reciprocal change over time.Dev Psychopathol. 2015 Nov;27(4 Pt 1):969-86. doi: 10.1017/S0954579415000632. Dev Psychopathol. 2015. PMID: 26439057 Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental patterns of anger from infancy to middle childhood predict problem behaviors at age 8.Dev Psychol. 2018 Nov;54(11):2090-2100. doi: 10.1037/dev0000589. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Dev Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30265026 Free PMC article.
-
Social competence and social support as mediators between comorbid depressive and conduct problems and functional outcomes in middle school children.J Adolesc. 2009 Jun;32(3):535-53. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2008.06.011. Epub 2008 Aug 10. J Adolesc. 2009. PMID: 18694594 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental origins of early antisocial behavior.Dev Psychopathol. 2009 Fall;21(4):1095-109. doi: 10.1017/S095457940999006X. Dev Psychopathol. 2009. PMID: 19825259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative Affect and Child Internalizing Symptoms: The Mediating Role of Perfectionism.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2016 Jun;47(3):358-68. doi: 10.1007/s10578-015-0571-x. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2016. PMID: 26215173
-
Temperament moderates associations between exposure to stress and children's externalizing problems.Child Dev. 2013 Sep-Oct;84(5):1579-93. doi: 10.1111/cdev.12076. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Child Dev. 2013. PMID: 23438634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach TM. “Comorbidity” in child and adolescent psychiatry: Categorical and quantitative perspectives. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 1991a;1:1–8.
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4–18 and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry; 1991b.
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the Teacher’s Report Form and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry; 1991c.
-
- Achenbach TM, Howell CT, Quay HC, Conners CK. National survey of problems and competencies among four-to-sixteen-year-olds: Parents’ reports for normative and clinical samples. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development. 1991;56 Serial No. 225, Whole No. 3. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
