The role of the death-domain kinase RIP in tumour-necrosis-factor-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases
- PMID: 12776182
- PMCID: PMC1319199
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor854
The role of the death-domain kinase RIP in tumour-necrosis-factor-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases
Abstract
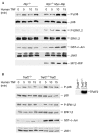
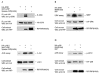
The death-domain kinase RIP (receptor-interacting protein) is an important effector of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) signalling and is essential for TNF-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation. However, the function of RIP in the TNF-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) has not been fully investigated. In this report, using Rip null (Rip(-/-)) mouse fibroblast cells, we investigated whether RIP is required for TNF-induced activation of the MAPKs extracellular-signal-related kinase (ERK), p38 and c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK). We found that TNF-induced activation of ERK, p38 and JNK is decreased in Rip(-/-) cells. The activation of these kinases by interleukin-1 is normal in Rip(-/-) cells. More importantly, we showed that the kinase activity of RIP is needed for ERK activation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The death domain kinase RIP is essential for TRAIL (Apo2L)-induced activation of IkappaB kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;20(18):6638-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.18.6638-6645.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10958661 Free PMC article.
-
The essential role of the death domain kinase receptor-interacting protein in insulin growth factor-I-induced c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation.J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 18;281(33):23525-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601487200. Epub 2006 Jun 22. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16793775
-
Tumor necrosis factor-induced nonapoptotic cell death requires receptor-interacting protein-mediated cellular reactive oxygen species accumulation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Mar 12;279(11):10822-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313141200. Epub 2003 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14701813
-
TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways.Semin Immunol. 2014 Jun;26(3):237-45. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24647229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor signaling.Cell Death Differ. 2003 Jan;10(1):45-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401189. Cell Death Differ. 2003. PMID: 12655295 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct signaling pathways in TRAIL- versus tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(21):8136-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00257-06. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16940186 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-interacting protein shuttles between cell death and survival signaling pathways.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Feb 1;21(3):481-8. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-06-0530. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 19955213 Free PMC article.
-
Proanthocyanidin-Rich Fractions from Red Rice Extract Enhance TNF-α-Induced Cell Death and Suppress Invasion of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell A549.Molecules. 2019 Sep 18;24(18):3393. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183393. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31540489 Free PMC article.
-
The function of TRADD in signaling through tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptors.Nat Immunol. 2008 Sep;9(9):1047-54. doi: 10.1038/ni.1639. Epub 2008 Jul 20. Nat Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18641653 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathways and Animal Models of Cardiomyopathies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1441:991-1019. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44087-8_64. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38884766
References
-
- Davis R.J. (1999) Signal transduction by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Biochem. Soc. Symp., 64, 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Devin A., Cook A., Lin Y., Rodriguez Y., Kelliher M. & Liu Z.G. (2000) The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity, 12, 419–429. - PubMed
-
- Holler N., Zaru R., Micheau O., Thome M., Attinger A., Valitutti S., Bodmer J.L., Schneider P., Seed B. & Tschopp J. (2000) Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nature Immunol., 1, 489–495. - PubMed
-
- Hsu H., Shu H.B., Pan M.G. & Goeddel D.V. (1996a) TRADD–TRAF2 and TRADD–FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell, 84, 299–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

