Stimulation of c-MYC transcriptional activity and acetylation by recruitment of the cofactor CBP
- PMID: 12776737
- PMCID: PMC1319176
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor821
Stimulation of c-MYC transcriptional activity and acetylation by recruitment of the cofactor CBP
Abstract
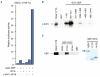
The c-MYC oncoprotein regulates various aspects of cell behaviour by modulating gene expression. Here, we report the identification of the cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CBP) as a novel c-MYC binding partner. The two proteins interact both in vitro and in cells, and CBP binds to the carboxy-terminal region of c-MYC. Importantly, CBP, as well as p300, is associated with E-box-containing promoter regions of genes that are regulated by c-MYC. Furthermore, c-MYC and CBP/p300 function synergistically in the activation of reporter-gene constructs. Thus, CBP and p300 function as positive cofactors for c-MYC. In addition, c-MYC is acetylated in cells. This modification does not require MYC box II, suggesting that it is independent of TRRAP complexes. Instead, CBP acetylates c-MYC in vitro, and co-expression of CBP with c-MYC stimulates in vivo acetylation. Functionally, this results in a decrease in ubiquitination and stabilization of c-MYC proteins. Thus, CBP and p300 are novel functional binding partners of c-MYC.
Figures
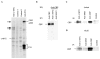



References
-
- Agalioti T., Chen G. & Thanos D. (2002) Deciphering the transcriptional histone acetylation code for a human gene. Cell, 111, 381–392. - PubMed
-
- Amati B., Frank S.R., Donjerkovic D. & Taubert S. (2001) Function of the c-Myc oncoprotein in chromatin remodeling and transcription. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1471, M135–M145. - PubMed
-
- Austen M., Cerni C., Lüscher-Firzlaff J.M. & Lüscher B. (1998) YY1 can inhibit c-Myc function through a mechanism requiring DNA binding of YY1 but neither its transactivation domain nor direct interaction with c-Myc. Oncogene, 17, 511–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

