Effects of leg muscle tendon vibration on group Ia and group II reflex responses to stance perturbation in humans
- PMID: 12777449
- PMCID: PMC2343054
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.043331
Effects of leg muscle tendon vibration on group Ia and group II reflex responses to stance perturbation in humans
Abstract
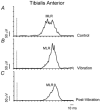
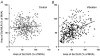
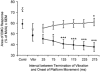
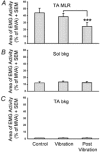
Stretching the soleus (Sol) muscle during sudden toe-up rotations of the supporting platform in a standing subject evokes a short-latency response (SLR) and a medium-latency response (MLR). The aim of the present investigation was to further explore the afferent and spinal pathways mediating the SLR and MLR in lower limb muscles by means of tendon vibration. In seven subjects, toe-up or toe-down rotations were performed under: (1) control, (2) continuous bilateral vibration at 90 Hz of Achilles' tendon or tibialis anterior (TA) tendon, and (3) post-vibration conditions. Sol and TA background EMG activity and reflex responses were bilaterally recorded and analysed. Toe-up rotations induced SLRs and MLRs in Sol at average latencies of 40 and 66 ms, respectively. During vibration, the latency of both responses increased by about 2 ms. The area of the SLR significantly decreased during vibration, regardless of the underlying background activity, and almost returned to control value post-vibration. The area of Sol MLR was less influenced by vibration than SLR, the reduction being negligible with relatively high background activity. However, contrary to SLR, MLR was even more reduced post-vibration. Toe-down rotations induced no SLR in the TA, while a MLR was evoked at about 81 ms. The area of TA MLR decreased slightly during vibration but much more post-vibration. SLRs and MLRs were differently affected by changing the vibration frequency to 30 Hz: vibration had a negligible effect on the SLR, but still produced a significant effect on the MLR. The independence from the background EMG of the inhibitory effect of vibration upon the SLR suggests that vibration removes a constant amount of the Ia afferent input. This can be accounted for by either presynaptic inhibition of group Ia fibres or a 'busy-line' phenomenon. The differential effect of vibration on SLRs and MLRs is compatible with the notions that spindle primaries have a higher sensitivity to vibration than secondaries, and that group II afferent fibres are responsible for the production of the MLR. The decrease of MLRs but not SLRs after vibration is discussed in terms of an interaction between peripheral and central drive on group II interneurones in order to produce sufficient EMG activity to maintain a given postural set.
Figures




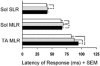
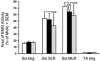

References
-
- Allum JHJ, Büdingen HJ. Coupled stretch reflexes in ankle muscles: an evaluation of the contributions of active muscle mechanisms to human postural stability. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:185–195. - PubMed
-
- Armitage P. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd; 1971.
-
- Ashby P, Stålberg E, Winkler T, Hunter JP. Further observations on the depression of group Ia facilitation of motoneurons by vibration in man. Exp Brain Res. 1987;69:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Bras H, Cavallari P, Jankowska E, Mccrea D. Comparison of effects of monoamines on transmission in spinal pathways from group and group II muscle afferents in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Burke D, Gandevia SC, McKeon B. Monosynaptic and oligosynaptic contributions to human ankle jerk and H-reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1984;52:435–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

