Predicting survival in patients with metastatic kidney cancer by gene-expression profiling in the primary tumor
- PMID: 12777628
- PMCID: PMC165812
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1131754100
Predicting survival in patients with metastatic kidney cancer by gene-expression profiling in the primary tumor
Abstract
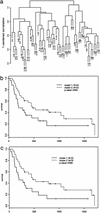
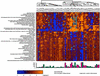
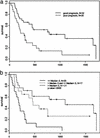
To identify potential molecular determinants of tumor biology and possible clinical outcomes, global gene-expression patterns were analyzed in the primary tumors of patients with metastatic renal cell cancer by using cDNA microarrays. We used grossly dissected tumor masses that included tumor, blood vessels, connective tissue, and infiltrating immune cells to obtain a gene-expression "profile" from each primary tumor. Two patterns of gene expression were found within this uniformly staged patient population, which correlated with a significant difference in overall survival between the two patient groups. Subsets of genes most significantly associated with survival were defined, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) was the gene most predictive for survival. Therefore, despite the complex biological nature of metastatic cancer, basic clinical behavior as defined by survival may be determined by the gene-expression patterns expressed within the compilation of primary gross tumor cells. We conclude that survival in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer can be correlated with the expression of various genes based solely on the expression profile in the primary kidney tumor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs with prognostic potential for metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a comparison of primary tumors and distant metastases.Ann Surg Oncol. 2014 Mar;21(3):1046-54. doi: 10.1245/s10434-013-3361-3. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24242678
-
Gene expression in kidney cancer is associated with cytogenetic abnormalities, metastasis formation, and patient survival.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jan 15;11(2 Pt 1):646-55. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15701852
-
MicroRNA profile in stage I clear cell renal cell carcinoma predicts progression to metastatic disease.Urol Oncol. 2020 Oct;38(10):799.e11-799.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2020.05.006. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Urol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32534961
-
[Microarrays for the identification of molecular markers in the diagnosis and therapy of renal cell carcinomas].Urologe A. 2006 Mar;45(3):297-8, 300-4. doi: 10.1007/s00120-006-1003-0. Urologe A. 2006. PMID: 16465525 Review. German.
-
[DNA and microRNA microarray technologies in diagnostics and prediction for patients with renal cell carcinoma].Klin Onkol. 2009;22(5):202-9. Klin Onkol. 2009. PMID: 19886357 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma.Target Oncol. 2010 Jun;5(2):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s11523-010-0143-8. Epub 2010 Jun 28. Target Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20582732 Review.
-
Staging of renal cell carcinoma: Current concepts.Indian J Urol. 2009 Oct-Dec;25(4):446-54. doi: 10.4103/0970-1591.57906. Indian J Urol. 2009. PMID: 19955666 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative genome-wide gene expression profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in Czech Republic and in the United States.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057886. Epub 2013 Mar 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23526956 Free PMC article.
-
The distribution, clearance, and safety of an anti-MMP-9 DNAzyme in normal and MMTV-PyMT transgenic mice.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013 Dec;23(6):379-88. doi: 10.1089/nat.2012.0348. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013. PMID: 24083396 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis-Initiating Cells in Renal Cancer.Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2014 Dec;8(3):240-246. doi: 10.2174/1574362409666140206222431. Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2014. PMID: 25152705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society (2002) Cancer Facts and Figures (Am. Cancer Soc., Atlanta).
-
- Vasselli, J. R., Yang, J. C., Linehan, W. M., White, D. E., Rosenberg, S. A. & Walther, M. M. (2001) J. Urol. 166, 68–72. - PubMed
-
- Wagner, J. R., Walther, M. M., Linehan, W. M., White, D. E., Rosenberg, S. A. & Yang, J. C. (1999) J. Urol. 162, 43–45. - PubMed
-
- Yang, J. C. & Rosenberg, S. A. (1997) Cancer J. Sci. Am. 3, Suppl. 1, S79–S84. - PubMed
-
- Lee, D. S., White, D. E., Hurst, R., Rosenberg, S. A. & Yang, J. C. (1998) Cancer J. Sci. Am. 4, 86–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

