Marine natural products and their potential applications as anti-infective agents
- PMID: 12781505
- PMCID: PMC7106398
- DOI: 10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00655-8
Marine natural products and their potential applications as anti-infective agents
Abstract
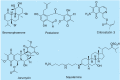
The oceans are a unique resource that provide a diverse array of natural products, primarily from invertebrates such as sponges, tunicates, bryozoans, and molluscs, and from marine bacteria and cyanobacteria. As infectious diseases evolve and develop resistance to existing pharmaceuticals, the marine environment provides novel leads against fungal, parasitic, bacterial, and viral diseases. Many marine natural products have successfully advanced to the late stages of clinical trials, including dolastatin 10, ecteinascidin-743, kahalalide F, and aplidine, and a growing number of candidates have been selected as promising leads for extended preclinical assessment. Although many marine-product clinical trials are for cancer chemotherapy, drug resistance, emerging infectious diseases, and the threat of bioterrorism have all contributed to the interest in assessing natural ocean products in the treatment of infectious organisms. In this review, we focus on the pharmacologically tested marine leads that have shown in-vivo efficacy or potent in-vitro activity against infectious and parasitic diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Marine sponges: potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009 Jan;10(1):86-105. doi: 10.2174/138920109787048625. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19149592 Review.
-
Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant fungal, viral, and parasitic infections.Lancet Infect Dis. 2017 Feb;17(2):e30-e41. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30323-1. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 27979695 Review.
-
Drugs from the sea: conotoxins as drug leads for neuropathic pain and other neurological conditions.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003 Nov;3(7):785-7. doi: 10.2174/1389557033487746. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14529519 Review.
-
Clinical status of anti-cancer agents derived from marine sources.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008 Aug;8(6):603-17. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18690825 Review.
-
Marine Pharmacology in 2012-2013: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action.Mar Drugs. 2017 Aug 29;15(9):273. doi: 10.3390/md15090273. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28850074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Marine natural products: a way to new drugs.Acta Naturae. 2009 Jul;1(2):15-25. Acta Naturae. 2009. PMID: 22649599 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Production of Bioactive Terrein by Aspergillus terreus Strain S020 Isolated from the Saudi Coast of the Red Sea.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 12;9(9):480. doi: 10.3390/biom9090480. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31547354 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the structure-activity relationship of marine natural polyketides as promising SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 22;11(50):31339-31363. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05817g. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496831 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Actinomycetes Associated with Stony Corals: A Potential Hotspot for Specialized Metabolites.Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 4;10(7):1349. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071349. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Antithrombotics.Mar Drugs. 2020 Oct 13;18(10):514. doi: 10.3390/md18100514. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33066214 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jimeno JM. A clinical armamentarium of marine-derived anti-cancer compounds. Anticancer Drugs. 2002;13(suppl 1):S15–S19. - PubMed
-
- Pomponi SA. The bioprocess-technological potential of the sea. J Biotechnol. 1999;70:5–13.
-
- Ireland CM, Copp BR, Foster MP, McDonald LA, Radisky DC, Swersey JC. Bioactive compounds from the sea. In: Martin RE, Carter EP, Davis LM, editors. Marine and freshwater products handbook. Technomic Publishing; Lanceaster. PA: 2000. pp. 641–661.
-
- Konig GM, Wright AD, Sticher O, Angerhofer CK, Pezzuto JM. Biological activities of selected marine natural products. Planta Med. 1994;60:532–537. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner DJ. Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 2001;18:1–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

