An angiogenic role for the human peptide antibiotic LL-37/hCAP-18
- PMID: 12782669
- PMCID: PMC156109
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI17545
An angiogenic role for the human peptide antibiotic LL-37/hCAP-18
Abstract
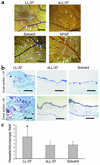
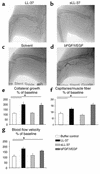
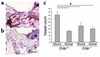
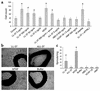
Antimicrobial peptides are effector molecules of the innate immune system and contribute to host defense and regulation of inflammation. The human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37/hCAP-18 is expressed in leukocytes and epithelial cells and secreted into wound and airway surface fluid. Here we show that LL-37 induces angiogenesis mediated by formyl peptide receptor-like 1 expressed on endothelial cells. Application of LL-37 resulted in neovascularization in the chorioallantoic membrane assay and in a rabbit model of hind-limb ischemia. The peptide directly activates endothelial cells, resulting in increased proliferation and formation of vessel-like structures in cultivated endothelial cells. Decreased vascularization during wound repair in mice deficient for CRAMP, the murine homologue of LL-37/hCAP-18, shows that cathelicidin-mediated angiogenesis is important for cutaneous wound neovascularization in vivo. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that LL-37/hCAP-18 is a multifunctional antimicrobial peptide with a central role in innate immunity by linking host defense and inflammation with angiogenesis and arteriogenesis.
Figures
Comment in
-
What is the real role of antimicrobial polypeptides that can mediate several other inflammatory responses?J Clin Invest. 2003 Jun;111(11):1643-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI18761. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12782665 Free PMC article. Review.
Similar articles
-
Human endogenous antibiotic LL-37 stimulates airway epithelial cell proliferation and wound closure.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005 Nov;289(5):L842-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00286.2004. Epub 2005 Jun 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15964896
-
Transient cutaneous adenoviral gene therapy with human host defense peptide hCAP-18/LL-37 is effective for the treatment of burn wound infections.Gene Ther. 2005 Oct;12(20):1494-502. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302568. Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15973442
-
LL-37, the neutrophil granule- and epithelial cell-derived cathelicidin, utilizes formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) as a receptor to chemoattract human peripheral blood neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells.J Exp Med. 2000 Oct 2;192(7):1069-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.7.1069. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 11015447 Free PMC article.
-
What is the real role of antimicrobial polypeptides that can mediate several other inflammatory responses?J Clin Invest. 2003 Jun;111(11):1643-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI18761. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12782665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human cathelicidin LL-37: a multifunctional peptide involved in infection and inflammation in the lung.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005;18(5):321-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2005.01.001. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15939310 Review.
Cited by
-
The Antimicrobial Peptide Cathelicidin Exerts Immunomodulatory Effects via Scavenger Receptors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):875. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010875. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614313 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Lipid and Metal Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Peptide Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Nov 8;11(11):588. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11110588. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31717337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCR2 specific endocytosis of immunomodulatory peptide LL-37 in human monocytes and formation of LL-37 positive large vesicles in differentiated monoosteophils.Bone Rep. 2019 Dec 13;12:100237. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2019.100237. eCollection 2020 Jun. Bone Rep. 2019. PMID: 31886324 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis of airway epithelial cells: human serum sensitive induction by the cathelicidin LL-37.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Apr;34(4):399-409. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0170OC. Epub 2005 Dec 9. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16340000 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Vascularization of Biomaterials for Skin and Bone Regeneration by Surface Modification: A Narrative Review on Experimental Research.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Jul 4;9(7):298. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9070298. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35877349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ganz T. Defensins and host defense. Science. 1999;286:420–421. - PubMed
-
- Zanetti M, Gennaro R, Romeo D. Cathelicidins: a novel protein family with a common proregion and a variable C-terminal antimicrobial domain. FEBS Lett. 1995;374:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Agerberth B, et al. The human antimicrobial and chemotactic peptides LL-37 and alpha-defensins are expressed by specific lymphocyte and monocyte populations. Blood. 2000;96:3086–3093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

