MIF signal transduction initiated by binding to CD74
- PMID: 12782713
- PMCID: PMC2193907
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030286
MIF signal transduction initiated by binding to CD74
Abstract
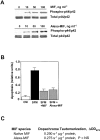
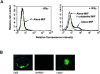
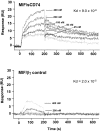
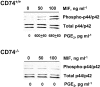
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) accounts for one of the first cytokine activities to have been described, and it has emerged recently to be an important regulator of innate and adaptive immunity. MIF is an upstream activator of monocytes/macrophages, and it is centrally involved in the pathogenesis of septic shock, arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions. The protein is encoded by a unique but highly conserved gene, and X-ray crystallography studies have shown MIF to define a new protein fold and structural superfamily. Although recent work has begun to illuminate the signal transduction pathways activated by MIF, the nature of its membrane receptor has not been known. Using expression cloning and functional analysis, we report herein that CD74, a Type II transmembrane protein, is a high-affinity binding protein for MIF. MIF binds to the extracellular domain of CD74, and CD74 is required for MIF-induced activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 MAP kinase cascade, cell proliferation, and PGE2 production. A recombinant, soluble form of CD74 binds MIF with a dissociation constant of approximately 9 x 10-9 Kd, as defined by surface plasmon resonance (BIAcore analysis), and soluble CD74 inhibits MIF-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in defined cell systems. These data provide a molecular basis for MIF's interaction with target cells and identify it as a natural ligand for CD74, which has been implicated previously in signaling and accessory functions for immune cell activation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of the JNK signalling pathway by macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and dependence on CXCR4 and CD74.Cell Signal. 2011 Jan;23(1):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.08.013. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 20807568 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 is the signaling component of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor-CD74 receptor complex.Immunity. 2006 Oct;25(4):595-606. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.08.020. Immunity. 2006. PMID: 17045821 Free PMC article.
-
Both host and parasite MIF molecules bind to chicken macrophages via CD74 surface receptor.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Dec;47(2):319-26. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.07.021. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25086294
-
MIF, CD74 and other partners in kidney disease: tales of a promiscuous couple.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Feb;24(1):23-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.08.001. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 22959722 Review.
-
Insight into the biology of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) revealed by the cloning of its cell surface receptor.Cell Res. 2006 Feb;16(2):162-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310022. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16474429 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor during dengue virus infection.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:547094. doi: 10.1155/2015/547094. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25821355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterocomplexes between the atypical chemokine MIF and the CXC-motif chemokine CXCL4L1 regulate inflammation and thrombus formation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Sep 12;79(10):512. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04539-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36094626 Free PMC article.
-
CD74 is a functional MIF receptor on activated CD4+ T cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jul 11;81(1):296. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05338-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38992165 Free PMC article.
-
A novel immune prognostic model of non-M3 acute myeloid leukemia.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Aug 15;14(8):5308-5325. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36105048 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Iguratimod as an Inhibitor of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) with Steroid-sparing Potential.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 16;291(51):26502-26514. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.743328. Epub 2016 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27793992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- George, M., and J.H. Vaughn. 1962. In vitro cell migration as a model for delayed hypersensitivity. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 111:514–521. - PubMed
-
- Bloom, B.R., and B. Bennett. 1966. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science. 153:80–82. - PubMed
-
- Bernhagen, J., T. Calandra, R.A. Mitchell, S.B. Martin, K.J. Tracey, W. Voelter, K.R. Manogue, A. Cerami, and R. Bucala. 1993. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 365:756–759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

