An alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell growth induced by IP-10, Mig, and I-TAC, and acts as functional receptor for platelet factor 4
- PMID: 12782716
- PMCID: PMC2193908
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021897
An alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell growth induced by IP-10, Mig, and I-TAC, and acts as functional receptor for platelet factor 4
Abstract
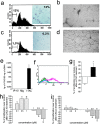
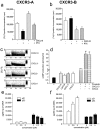
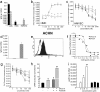
The chemokines CXCL9/Mig, CXCL10/IP-10, and CXCL11/I-TAC regulate lymphocyte chemotaxis, mediate vascular pericyte proliferation, and act as angiostatic agents, thus inhibiting tumor growth. These multiple activities are apparently mediated by a unique G protein-coupled receptor, termed CXCR3. The chemokine CXCL4/PF4 shares several activities with CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11, including a powerful angiostatic effect, but its specific receptor is still unknown. Here, we describe a distinct, previously unrecognized receptor named CXCR3-B, derived from an alternative splicing of the CXCR3 gene that mediates the angiostatic activity of CXCR3 ligands and also acts as functional receptor for CXCL4. Human microvascular endothelial cell line-1 (HMEC-1), transfected with either the known CXCR3 (renamed CXCR3-A) or CXCR3-B, bound CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11, whereas CXCL4 showed high affinity only for CXCR3-B. Overexpression of CXCR3-A induced an increase of survival, whereas overexpression of CXCR3-B dramatically reduced DNA synthesis and up-regulated apoptotic HMEC-1 death through activation of distinct signal transduction pathways. Remarkably, primary cultures of human microvascular endothelial cells, whose growth is inhibited by CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, and CXCL4, expressed CXCR3-B, but not CXCR3-A. Finally, monoclonal antibodies raised to selectively recognize CXCR3-B reacted with endothelial cells from neoplastic tissues, providing evidence that CXCR3-B is also expressed in vivo and may account for the angiostatic effects of CXC chemokines.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cell cycle-dependent expression of CXC chemokine receptor 3 by endothelial cells mediates angiostatic activity.J Clin Invest. 2001 Jan;107(1):53-63. doi: 10.1172/JCI9775. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11134180 Free PMC article.
-
CCR3 functional responses are regulated by both CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Aug;33(8):2241-50. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323787. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12884299
-
Molecular characterization of the chemokine receptor CXCR3: evidence for the involvement of distinct extracellular domains in a multi-step model of ligand binding and receptor activation.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Oct;33(10):2927-36. doi: 10.1002/eji.200324235. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14515277
-
CXCR3-binding chemokines: novel multifunctional therapeutic targets.Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2005 Mar;5(1):109-18. doi: 10.2174/1568008053174723. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2005. PMID: 15777209 Review.
-
CXCR3 Ligands in Cancer and Autoimmunity, Chemoattraction of Effector T Cells, and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2020 May 29;11:976. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00976. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32547545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CXCR3 in carcinoma progression.Histol Histopathol. 2015 Jul;30(7):781-92. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-594. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Histol Histopathol. 2015. PMID: 25663474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in the progression and treatment of tumors.J Mol Histol. 2012 Dec;43(6):699-713. doi: 10.1007/s10735-012-9435-x. Epub 2012 Jun 30. J Mol Histol. 2012. PMID: 22752457 Review.
-
Chemokine receptor trio: CXCR3, CXCR4 and CXCR7 crosstalk via CXCL11 and CXCL12.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Feb;24(1):41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 16. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 22989616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of the chemokines CXCL11 and CXCL12 in human tumor cells.BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec 20;22(1):1335. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10451-4. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36539774 Free PMC article.
-
Angiostatic and chemotactic activities of the CXC chemokine CXCL4L1 (platelet factor-4 variant) are mediated by CXCR3.Blood. 2011 Jan 13;117(2):480-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-253591. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Blood. 2011. PMID: 20980681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zlotnik, A., and O. Yoshie. 2000. Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity. 12:121–127. - PubMed
-
- Rossi, D., and A. Zlotnik. 2000. The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:217–242. - PubMed
-
- Grone, H.J., C.D. Cohen, E. Grone, C. Schmidt, M. Kretzler, D. Schlondorff, and P.J. Nelson. 2002. Spatial and temporally restricted expression of chemokines and chemokine receptors in the developing human kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13:957–967. - PubMed
-
- Belperio, J.A., M.P. Keane, D.A. Arenberg, C.L. Addison, J.E. Ehlert, M.D. Burdick, and R.M. Strieter. 2000. CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 68:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Homey, B., A. Müller, and A. Zlotnik. 2002. Chemokines: agents for the immunotherapy of cancer? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:175–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

