Retinoid activation of retinoic acid receptor but not retinoid X receptor is sufficient to rescue lethal defect in retinoic acid synthesis
- PMID: 12782789
- PMCID: PMC165842
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1231422100
Retinoid activation of retinoic acid receptor but not retinoid X receptor is sufficient to rescue lethal defect in retinoic acid synthesis
Abstract
Two isomers of retinoic acid (RA) may be necessary as ligands for retinoid signaling: all-trans-RA for RA receptors (RARs) and 9-cis-RA for retinoid X receptors (RXRs). This was explored by using retinaldehyde dehydrogenase (Raldh)2-/- mouse embryos lacking mesodermal RA synthesis that display early growth arrest unless rescued by all-trans-RA administration. Because isomerization of all-trans-RA to 9-cis-RA can occur, it is unclear whether both ligands are needed for rescue. We show here that an RAR-specific ligand can rescue Raldh2-/- embryos as efficiently as all-trans-RA, whereas an RXR-specific ligand has no effect. Further, whereas all-trans-RA was detected in embryos, 9-cis-RA was undetectable unless a supraphysiological dose of all-trans-RA was administered, revealing that 9-cis-RA is of pharmacological but not physiological significance. Because 9-cis-RA is undetectable and unnecessary for Raldh2-/- rescue, and others have shown that 4-oxo-RA is unnecessary for mouse development, all-trans-RA emerges as the only ligand clearly necessary for retinoid receptor signaling.
Figures
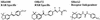

References
-
- Clagett-Dame, M. & DeLuca, H. F. (2002) Annu. Rev. Nutr. 22, 347-381. - PubMed
-
- Mangelsdorf, D. J., Ong, E. S., Dyck, J. A. & Evans, R. M. (1990) Nature 345, 224-229. - PubMed
-
- Petkovich, M., Brand, N. J., Krust, A. & Chambon, P. (1987) Nature 330, 444-450. - PubMed
-
- Giguère, V., Ong, E. S., Segui, P. & Evans, R. M. (1987) Nature 330, 624-629. - PubMed
-
- Levin, A. A., Sturzenbecker, L. J., Kazmer, S., Bosakowski, T., Huselton, C., Allenby, G., Speck, J., Kratzeisen, C., Rosenberger, M., Lovey, A. & Grippo, J. F. (1992) Nature 355, 359-361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

