Chronic mild hypoxia protects heart-derived H9c2 cells against acute hypoxia/reoxygenation by regulating expression of the SUR2A subunit of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel
- PMID: 12791696
- PMCID: PMC2134977
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M303051200
Chronic mild hypoxia protects heart-derived H9c2 cells against acute hypoxia/reoxygenation by regulating expression of the SUR2A subunit of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel
Abstract
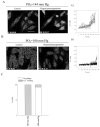
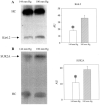
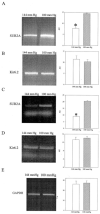
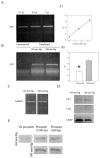
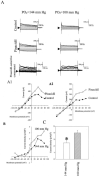
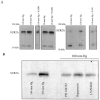
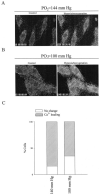
Chronic exposure to lower oxygen tension may increase cellular resistance to different types of acute metabolic stress. Here, we show that 24-h-long exposure to slightly decreased oxygen tension (partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) of 100 mm Hg instead of normal 144 mm Hg) confers resistance against acute hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced Ca2+ loading in heart-derived H9c2 cells. The number of ATP-sensitive K+ (K(ATP)) channels were increased in cells exposed to PO2 = 100 mm Hg relative to cells exposed to PO2 = 144 mm Hg. This was due to an increase in transcription of SUR2A, a K(ATP) channel regulatory subunit, but not Kir6.2, a K(ATP) channel pore-forming subunit. PO2 = 100 mm Hg also increased the SUR2 gene promoter activity. Experiments with cells overexpressing wild type of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and dominant negative HIF-1beta suggested that the HIF-1-signaling pathway did not participate in observed PO2-mediated regulation of SUR2A expression. On the other hand, NADH inhibited the effect of PO2 = 100 mm Hg but not the effect of PO2 = 20 mm Hg. LY 294002 and PD 184 352 prevented PO2-mediated regulation of K(ATP) channels, whereas rapamycin was without any effect. HMR 1098 inhibited the cytoprotective effect of PO2 = 100 mm Hg, and a decrease of PO2 from 144 to 100 mm Hg did not change the expression of any other gene, including those involved in stress and hypoxic response, as revealed by Affymetrix high density oligonucleotide arrays. We conclude that slight hypoxia activates HIF-1alpha-independent signaling cascade leading to an increase in SUR2A protein, a higher density of K(ATP) channels, and a cellular phenotype more resistant to acute metabolic stress.
Figures


References
-
- Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002;192:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Wenger RH. FASEB J. 2002;16:1151–1162. - PubMed
-
- Silverman HS, Wei S, Haigney MC, Ocampo CJ, Stern MD. Circ. Res. 1997;80:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Ashouri K, Ahmed ME, Kardash MO, Sharif AY, Abdalsattar M, al Ghozeim A. Ethn. Dis. 1994;4:82–86. - PubMed
-
- Hutchison SJ, Litch JA. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1997;278:1661–1662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

