Emergence of rifampin-resistant Rhodococcus equi with several types of mutations in the rpoB gene among AIDS patients in northern Thailand
- PMID: 12791846
- PMCID: PMC156560
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2337-2340.2003
Emergence of rifampin-resistant Rhodococcus equi with several types of mutations in the rpoB gene among AIDS patients in northern Thailand
Abstract
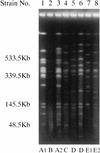
The antimicrobial susceptibilities of 30 Rhodococcus equi isolates obtained from 30 patients between 1993 and 2001 in northern Thailand were investigated. The MICs showed a tendency toward resistance to various antibiotics but sensitivity to imipenem, minocycline, vancomycin, and teicoplanin (MICs, </=0.5 micro g/ml) and relative sensitivity to meropenem, clarithromycin, and ciprofloxacin (MICs, </=2 micro g/ml). Of the 30 isolates, 26 were susceptible (MICs, </=1 micro g/ml), 1 showed low-level resistance (MIC, 8 micro g/ml), and 3 showed high-level resistance (MICs, >/=64 micro g/ml) to rifampin. PCR amplification and DNA sequencing of the rpoB gene and molecular typing by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) were performed for eight R. equi isolates from eight AIDS patients with pneumonia or lung abscess caused by R. equi between 1998 and 2001, including one low- and three high-level rifampin-resistant isolates. As a result, two high-level rifampin-resistant strains with PFGE pattern A had a Ser531Trp (Escherichia coli numbering) mutation, and one high-level rifampin-resistant strain with PFGE pattern B had a His526Tyr mutation, whereas one low-level rifampin-resistant strain with PFGE pattern C had a Ser509Pro mutation. Four rifampin-susceptible strains with PFGE patterns D and E showed an absence of mutation in the rpoB region. Our results indicate the presence of several types of rifampin-resistant R. equi strains among AIDS patients in northern Thailand.
Figures
References
-
- Chariyalertsak, S., T. Sirisanthana, O. Saengwonloey, and K. E. Nelson. 2001. Clinical presentation and risk behaviors of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in Thailand, 1994-1998: regional variation and temporal trends. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32:955-962. - PubMed
-
- Donisi, A., M. G. Suardi, S. Casari, M. Longo, G. P. Cadeo, and G. Carosi. 1996. Rhodococcus equi infection in HIV-infected patients. AIDS 10:359-362. - PubMed
-
- Drancourt, M., E. Bonnet, H. Gallais, Y. Peloux, and D. Raoult. 1992. Rhodococcus equi infection in patients with AIDS. J. Infect. 24:123-131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

