Novel reporter T-cell line highly susceptible to both CCR5- and CXCR4-using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and its application to drug susceptibility tests
- PMID: 12791875
- PMCID: PMC156554
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2515-2521.2003
Novel reporter T-cell line highly susceptible to both CCR5- and CXCR4-using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and its application to drug susceptibility tests
Abstract
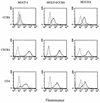
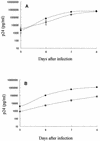
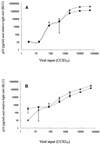
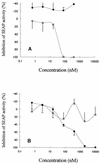
CCR5-using (R5) human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is a major viral population that is transmitted by sexual intercourse and that replicates in infected individuals during the asymptomatic stage of HIV-1 infection, suggesting that agents effective against R5 HIV-1 can be expected to prevent viral transmission and delay disease progression. However, R5 HIV-1 is unable to replicate in human T-cell lines, which is an apparent obstacle to efficient and reliable susceptibility tests of compounds for their activities against R5 HIV-1. To establish a simple and rapid assay system for the monitoring of R5 HIV-1 replication and drug susceptibility, we have established a novel reporter T-cell line, MOCHA (which represents MOLT-4 cells stably expressing CCR5 and carrying the HIV-1 long terminal repeat-driven secretory alkaline phosphatase). Cells of this cell line express CD4, CXCR4, and CCR5 on their surfaces and secrete human placental alkaline phosphatase into the culture supernatants during HIV-1 infection. MOCHA cells proved to be highly permissive for the replication of R5 HIV-1 as well as CXCR4-using (X4) HIV-1, and the alkaline phosphatase activity increased in parallel with increasing HIV-1 p24 antigen levels in the culture supernatants. When HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors, protease inhibitors, and entry inhibitors, including the CCR5 antagonist TAK-779 and the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100, were examined for their inhibitory effects on R5 and X4 HIV-1 replication in MOCHA cells, the antiviral activities of these compounds were found to be almost identical to those previously reported in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Thus, MOCHA cells are an extremely useful tool for detection of R5 and X4 HIV-1 replication and drug susceptibility tests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Use of new T-cell-based cell lines expressing two luciferase reporters for accurately evaluating susceptibility to anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 drugs.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;45(2):477-87. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01708-06. Epub 2006 Dec 20. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17182760 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a CCR5-expressing T-lymphoblastoid cell line highly susceptible to R5 HIV type 1.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Jul 1;16(10):935-41. doi: 10.1089/08892220050058344. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 10890354
-
A novel colorimetric assay for CXCR4 and CCR5 tropic human immunodeficiency viruses.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2006;17(4):215-23. doi: 10.1177/095632020601700405. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2006. PMID: 17066899
-
HIV co-receptors as targets for antiviral therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2004;4(9):883-93. doi: 10.2174/1568026043388501. Curr Top Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15134547 Review.
-
HIV chemokine receptor inhibitors as novel anti-HIV drugs.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005 Dec;16(6):659-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.05.009. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005. PMID: 16005254 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of new T-cell-based cell lines expressing two luciferase reporters for accurately evaluating susceptibility to anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 drugs.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;45(2):477-87. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01708-06. Epub 2006 Dec 20. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17182760 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) full replication assay that includes HIV-1 Vif as an antiviral target.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Sep;49(9):3833-41. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.9.3833-3841.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16127060 Free PMC article.
-
TILRR Promotes Migration of Immune Cells Through Induction of Soluble Inflammatory Mediators.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 3;8:563. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00563. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32719797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arenzana-Seisdedos, F., J.-L. Virelizier, D. Rousset, I. Clark-Lewis, P. Loetscher, B. Moser, and M. Baggiolini. 1996. HIV blocked by chemokine antagonist. Nature 383:400. - PubMed
-
- Baba, M., H. Miyake, M. Okamoto, Y. Iizawa, and K. Okonogi. 2000. Establishment of a CCR5-expressing T-lymphoblastoid cell line highly susceptible to R5 HIV type 1. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 16:935-941. - PubMed
-
- Baba, M., O. Nishimura, N. Kanzaki, M. Okamoto, H. Sawada, Y. Iizawa, M. Shiraishi, Y. Aramaki, K. Okonogi, Y. Ogawa, K. Meguro, and M. Fujino. 1999. A small-molecule, nonpeptide CCR5 antagonist with highly potent and selective anti-HIV-1 activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:5698-5703. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger, J., J. Hauber, R. Hauber, R. Geiger, and B. R. Cullen. 1988. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene 66:1-10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

