Multilocus sequence typing system for group B streptococcus
- PMID: 12791877
- PMCID: PMC156480
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2530-2536.2003
Multilocus sequence typing system for group B streptococcus
Abstract
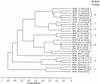
A multilocus sequence typing (MLST) system was developed for group B streptococcus (GBS). The system was used to characterize a collection (n = 152) of globally and ecologically diverse human strains of GBS that included representatives of capsular serotypes Ia, Ib, II, III, V, VI, and VIII. Fragments (459 to 519 bp) of seven housekeeping genes were amplified by PCR for each strain and sequenced. The combination of alleles at the seven loci provided an allelic profile or sequence type (ST) for each strain. A subset of the strains were characterized by restriction digest patterning, and these results were highly congruent with those obtained with MLST. There were 29 STs, but 66% of isolates were assigned to four major STs. ST-1 and ST-19 were significantly associated with asymptomatic carriage, whereas ST-23 included both carried and invasive strains. All 44 isolates of ST-17 were serotype III clones, and this ST appeared to define a homogeneous clone that was strongly associated with neonatal invasive infections. The finding that isolates with different capsular serotypes had the same ST suggests that recombination occurs at the capsular locus. A web site for GBS MLST was set up and can be accessed at http://sagalactiae.mlst.net. The GBS MLST system offers investigators a valuable typing tool that will promote further investigation of the population biology of this organism.
Figures

References
-
- Bliss, S. J., S. D. Manning, P. Tallman, C. J. Baker, M. D. Pearlman, C. F. Marrs, and B. Foxman. 2002. Group B streptococcus colonization in male and nonpregnant female university students: a cross-sectional prevalence study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:184-190. - PubMed
-
- Bohnsack, J. F., S. Takahashi, S. R. Detrick, L. R. Pelinka, L. L. Hammitt, A. A. Aly, A. A. Whiting, and E. E. Adderson. 2001. Phylogenetic classification of serotype III group B streptococci on the basis of hylB gene analysis and DNA sequences specific to restriction digest pattern type III-3. J. Infect. Dis. 183:1694-1697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

