Prevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 among blood donors from Mashhad, Iran
- PMID: 12791885
- PMCID: PMC156501
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2593-2595.2003
Prevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 among blood donors from Mashhad, Iran
Abstract
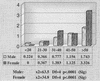
The city of Mashhad is the capital of Khorasan, the northeastern province of Iran, which has been recognized as an area where human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection is endemic. All serum samples from blood donors are routinely screened for HTLV-1 by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In the present study, 28,926 donors (81.86% male and 18.14% female) with a mean age of 32 years (range, 18 to 65 years) were screened in a 6 months period (July to December 1999). Of these donors in the primary screening, 228 (0.78%) tested positive by ELISA. The positive samples were confirmed by Western blot (WB) analysis. The WB results indicated that, of 228 positive ELISA specimens, 91.2% (208 specimens) were HTLV-1, 4.82% (11 specimens) were HTLV, 3.5% (8 specimens) were indeterminate, and 0.44% (1 specimen) was not confirmed. HTLV refers to samples in which the complete viral antigen banding patterns on WB strips were not present. In order to further evaluate the detection methodologies used, the HTLV-1-seropositive samples, the indeterminant samples, and/or HTLV samples were examined and confirmed by PCR. The HTLV samples were determined to be HTLV-1, the remaining samples were indeterminant, and the negative sample could not be confirmed for HTLV-1 by PCR. The prevalence of HTLV-1 infection in our study was 0.77% among blood bank donors, which reconfirms the city of Mashhad as an area where the virus is endemic compared to other regions in the world. The incidence was correlated with increasing age, and it was higher in females than in males.
Figures

References
-
- Blattner, W. A., K. Takatsuki, and R. C. Gallo. 1983. Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus and adult T-cell leukemia. JAMA 250:1074-1080. - PubMed
-
- Gessain, A., E. Barin, J. C. Vernant, O. Gout, L. Maurs, A. Calender, and G. de The. 1985. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-1 in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet ii:407-410. - PubMed
-
- Hjelle, B., R. Mills, G. Mertz, and S. Swenson. 1990. Transmission of HTLV-1 via blood transfusion. Vox Sang. 59:119-122. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

