Genetic diversity of Gallibacterium anatis isolates from different chicken flocks
- PMID: 12791918
- PMCID: PMC156494
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2737-2740.2003
Genetic diversity of Gallibacterium anatis isolates from different chicken flocks
Abstract
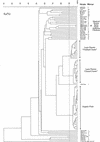
Amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLPs) were used to characterize the genotypic diversity of a total of 114 Gallibacterium anatis isolates originating from a reference collection representing 15 biovars from four countries and isolates obtained from tracheal and cloacal swab samples of chickens from an organic, egg-producing flock and a layer parent flock. A subset of strains was also characterized by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and biotyping. The organic flock isolates were characterized by more than 94% genetic similarity, indicating that only a single clone was apparent in the flock. The layer parent flock isolates were grouped into two subclusters, each with similarity above 90%. One subcluster contained only tracheal isolates, while the other primarily included cloacal isolates. In conclusion, we show that AFLP analysis enables fingerprinting of G. anatis, which seems to have a clonal population structure within natural populations. There was further evidence of clonal lineages, which may have adapted to different sites within the same animal.
Figures
References
-
- Aalbaek, B., L. Eriksen, R. B. Rimler, P. S. Leifsson, A. Basse, T. Christiansen, and E. Eriksen. 1999. Typing of Pasteurella multocida from haemorrhagic septicaemia in Danish fallow deer (Dama dama). APMIS 107:913-920. - PubMed
-
- Bisgaard, M. 1982. Isolation and characterization of some previously unreported taxa from poultry with phenotypical characters related to Actinobacillus- and Pasteurella species. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. Sect. B 90:59-67. - PubMed
-
- Bisgaard, M. 1977. Incidence of Pasteurella haemolytica in the respiratory tract of apparently healthy chickens and chickens with infectious bronchitis. Characterisation of 213 strains. Avian Pathol. 6:285-292. - PubMed
-
- Bisgaard, M. 1993. Ecology and significance of Pasteurellaceae in animals. Zentbl. Bakteriol. 279:7-26. - PubMed
-
- Bisgaard, M., and A. Dam. 1981. Salpingitis in poultry. II. Prevalence, bacteriology, and possible pathogenesis in egg-laying chickens. Nord. Vetmed. 33:81-89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

