Identification of a functionally relevant cannabinoid receptor on mouse spleen cells that is involved in cannabinoid-mediated immune modulation
- PMID: 1279376
- PMCID: PMC3657723
Identification of a functionally relevant cannabinoid receptor on mouse spleen cells that is involved in cannabinoid-mediated immune modulation
Abstract
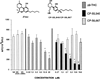
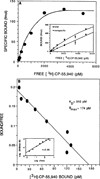
Extensive behavioral and biochemical characterization of cannabinoid-mediated effects on the central nervous system has revealed at least three lines of evidence supporting the role of a putative guanine nucleotide-binding protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor for cannabimimetic effects, (i) stereoselectivity, (ii) inhibition of the adenylate cyclase/cAMP second messenger system, and (iii) radioligand-binding studies with the synthetic cannabinoid [3H]CP-55,940 indicating a high degree of specific binding to brain tissue preparations. Based on recent findings from our laboratory demonstrating that delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol markedly inhibited forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in mouse spleen cells, the presence of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor associated with mouse spleen cells and its functional role in immune modulation were investigated. In the present studies, stereoselective immune modulation was observed with the synthetic bicyclic cannabinoid (-)-CP-55,940 versus (+) CP-56,667 and with 11-OH-delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol-dimethylheptyl, (-)-HU-210 versus (+)-HU-211. In both cases, the (-)-enantiomer demonstrated greater immunoinhibitory potency than the (+)-isomer, as measured by the in vitro sheep red blood cell antibody-forming cell response. Radioligand binding studies produced a saturation isotherm exhibiting approximately 45-65% specific binding to mouse spleen cells. Scatchard analysis demonstrated a single binding site on spleen cells, possessing a Kd of 910 pM and a Bmax of approximately 1000 receptors/spleen cell. RNA polymerase chain reaction of isolated splenic RNA using specific primers for the cannabinoid receptor resulted in the amplification of a 854-kilobase predicted product that hybridized with cannabinoid receptor cDNA, demonstrating the presence of cannabinoid receptor mRNA in mouse spleen. Together, these findings strongly support the role of a cannabinoid receptor in immune modulation by cannabimimetic agents.
Figures


References
-
- Munson AE, Fehr KO. Immunological effects of cannabis. In: Fehr KO, Kalant H, editors. Adverse Health and Behavioral Consequences of Cannabis Us. Addiction Research Foundation; 1983. pp. 257–353.
-
- Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature (Lond.) 1990;346:561–564. - PubMed
-
- Howlett AC, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, Milne GM. Nonclassical cannabinoid analgetics inhibit adenylate cyclase: development of a cannabinoid receptor model. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988;23:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Devane WA, Dysarz FA, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, Howlett AC. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988;34:605–613. - PubMed
-
- Little PJ, Compton DR, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, Martin BR. Pharmacology and stereoselectivity of structurally novel cannabinoids in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1988;247:1046–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
