Calcineurin is essential for Candida albicans survival in serum and virulence
- PMID: 12796287
- PMCID: PMC161442
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.2.3.422-430.2003
Calcineurin is essential for Candida albicans survival in serum and virulence
Abstract
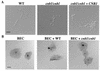
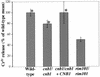
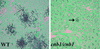
Calcineurin is a calcium-activated protein phosphatase that is the target of the immunosuppressants cyclosporin A and FK506. In T cells, calcineurin controls nuclear import of the NF-AT transcription factor and gene activation. In plants and fungi, calcineurin functions in stress responses (e.g., temperature, cations, and pH) and is necessary for the virulence of the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. Here we show that calcineurin is also required for the virulence of another major fungus that is pathogenic to humans, Candida albicans. C. albicans calcineurin mutants had significantly reduced virulence in a murine model of systemic infection. In contrast to its role in C. neoformans, calcineurin was not required for C. albicans survival at 37 degrees C. Moreover, C. albicans calcineurin mutant strains exhibited no defects in known Candida virulence traits associated with host invasion, including filamentous growth, germ tube formation, and adherence to and injury of mammalian cells. C. albicans calcineurin mutant strains failed to colonize and grow in the kidneys of infected animals and were unable to survive when exposed to serum in vitro. Our studies illustrate that calcineurin has evolved to control aspects of the virulence of two divergent fungal pathogens via distinct mechanisms that can be targeted to achieve broad-spectrum antifungal action.
Figures
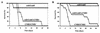

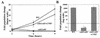
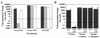
References
-
- Anaissie, E., H. Pinczowski, and D. Louria. 1993. Candida infections in experimental animals, p. 43-57. In G. Bodey (ed.), Candidiasis. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Raven Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Aramburu, J., A. Rao, and C. B. Klee. 2000. Calcineurin: from structure to function. Curr. Top. Cell Regul. 36:237-295. - PubMed
-
- Ashman, R., and J. Papadimitriou. 1989. Genetic regulation of pathogenesis and host responses in fungal infection, p. 347-371. In E. Kurstak and G. Marquis (ed.), Immunology of fungal infection. Marcel Dekker, New York, N.Y. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

