Histone-like proteins of the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii have homologies to bacterial DNA-binding proteins
- PMID: 12796310
- PMCID: PMC161454
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.2.3.646-650.2003
Histone-like proteins of the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii have homologies to bacterial DNA-binding proteins
Abstract
The dinoflagellates have very large genomes encoded in permanently condensed and histoneless chromosomes. Sequence alignment identified significant similarity between the dinoflagellate chromosomal histone-like proteins of Crypthecodinium cohnii (HCCs) and the bacterial DNA-binding and the eukaryotic histone H1 proteins. Phylogenetic analysis also supports the origin of the HCCs from histone-like proteins of bacteria.
Figures
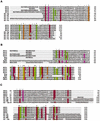

References
-
- Bendich, A. J., and K. Drlica. 2000. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes: what's the difference? Bioessays 22:481-486. - PubMed
-
- Bodansky, S., L. B. Mintz, and D. S. Holmes. 1979. The mesokaryote Gyrodinium cohnii lacks nucleosomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 88:1329-1336. - PubMed
-
- Bouligand, Y., and V. Norris. 2001. Chromosome separation and segregation in dinoflagellates and bacteria may depend on liquid crystalline states. Biochimie 83:187-192. - PubMed
-
- Cachon, J., H. Sato, M. Cachon, and Y. Sato. 1989. Analysis by polarizing microscopy of chromosomal structure among dinoflagellates and its phylogenetic involvement. Biol. Cell 65:51-60.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

