Development of a novel in vitro human tissue-based angiogenesis assay to evaluate the effect of antiangiogenic drugs
- PMID: 12796575
- PMCID: PMC1514676
- DOI: 10.1097/01.SLA.0000072111.53797.44
Development of a novel in vitro human tissue-based angiogenesis assay to evaluate the effect of antiangiogenic drugs
Abstract
Objective: To describe a novel in vitro human tissue-based angiogenic model that can predict an individual tumor's response to antiangiogenic drugs.
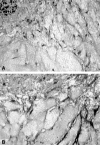
Summary background data: A number of in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis assays exist, but they do not provide potentially useful information for the treatment of an individual patient. Clonogenic assays have been used to evaluate the response of an individual's tumor to antineoplastic agents, but these tumor fragments are cultured in an environment that does not lead to neovessel growth. The authors have previously demonstrated that human vein disks or human tumor xenograft fragments incorporated into a 0.3% fibrin-thrombin clot will develop angiogenic vessel growth from the cut edge of the vessel disk or xenograft fragment.
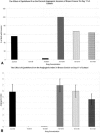
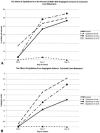
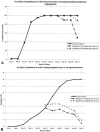
Methods: Fresh human tumor or normal tissue disks (2 x 1 mm) from fresh surgical specimens were incorporated into fibrin-thrombin clots overlain with nutrient medium containing either 20% fetal bovine serum alone or in combination with Epothilone B, a tubulin inhibitor with antiangiogenic properties. Tissue disks were visually assessed over time to determine the percentage of wells that developed an angiogenic response. Neovessel growth, density, and length were graded at intervals using a semiquantitative visual neovessel growth-rating scheme (angiogenic index, 0-16 scale) devised in the authors' laboratory.
Results: Epothilone B treatment at doses of 10-6 mol/L and 10-8 mol/L decreased the number of wells that developed an invasive angiogenic response and limited the development of vessels that invaded the matrix. At these doses, Epothilone B also caused regression of vessels in wells that had been allowed to develop an angiogenic response. Treatment of tumors or normal tissues with Epothilone B at doses less than 10-8 mol/L was ineffective.
Conclusions: Epothilone B may be an effective antiangiogenic agent in a variety of tumor types. The authors speculate that this in vitro model might provide useful information to the clinician on the effect of specific antiangiogenic agents on individual tumors. This may be particularly useful in patients with tumors that, as a group, are unresponsive to treatment with antineoplastic agents.
Figures
References
-
- Hamburger AW, Salmon SE. Primary bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science. 1977; 197: 461–463. - PubMed
-
- Kern DH, Weisenthal LM. Highly specific prediction of antineoplastic drug resistance with an in vitro assay using suprapharmacologic drug exposures. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990; 82: 582–588. - PubMed
-
- Costa SD, Lange S, Klinga K, et al. Factors influencing the prognostic role of oestrogen and progesterone receptor levels in breast cancer: results of the analysis of 670 patients with 11 years of follow-up. Eur J Cancer. 2002; 38: 1329–1334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

