Cadmium is a mutagen that acts by inhibiting mismatch repair
- PMID: 12796780
- PMCID: PMC2662193
- DOI: 10.1038/ng1172
Cadmium is a mutagen that acts by inhibiting mismatch repair
Abstract
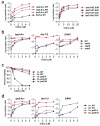
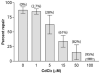
Most errors that arise during DNA replication can be corrected by DNA polymerase proofreading or by post-replication mismatch repair (MMR). Inactivation of both mutation-avoidance systems results in extremely high mutability that can lead to error catastrophe. High mutability and the likelihood of cancer can be caused by mutations and epigenetic changes that reduce MMR. Hypermutability can also be caused by external factors that directly inhibit MMR. Identifying such factors has important implications for understanding the role of the environment in genome stability. We found that chronic exposure of yeast to environmentally relevant concentrations of cadmium, a known human carcinogen, can result in extreme hypermutability. The mutation specificity along with responses in proofreading-deficient and MMR-deficient mutants indicate that cadmium reduces the capacity for MMR of small misalignments and base-base mismatches. In extracts of human cells, cadmium inhibited at least one step leading to mismatch removal. Together, our data show that a high level of genetic instability can result from environmental impediment of a mutation-avoidance system.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cancer, cadmium and genome integrity.Nat Genet. 2003 Jul;34(3):239-41. doi: 10.1038/ng0703-239. Nat Genet. 2003. PMID: 12833042 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schaaper RM. Base selection, proofreading, and mismatch repair during DNA replication in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:23762–23765. - PubMed
-
- Harfe BD, Jinks-Robertson S. DNA mismatch repair and genetic instability. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2000;34:359–399. - PubMed
-
- Peltomaki P. Deficient DNA mismatch repair: a common etiologic factor for colon cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001;10:735–740. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

