Correlation between power Doppler ultrasonography and clinical severity in Achilles tendinopathy
- PMID: 12799763
- PMCID: PMC3458440
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-002-0426-5
Correlation between power Doppler ultrasonography and clinical severity in Achilles tendinopathy
Abstract
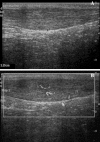
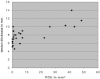
Twenty-five patients with chronic Achilles tendinopathy were clinically and ultrasonographically evaluated. A positive correlation existed between power Doppler ultrasonography (PDU) and tendon thickness (r=0.63, p<0.001) and patient's age (r=0.40, p<0.05). A negative correlation existed between PDU and a functional test (number of toe raises to pain) (r=-0.57, p<0.005) and one recorded item of the Victorian Institute of Sport Assessment Achilles score (VISA-A questionnaire, item 6: jumping capability) (r=-0.46, p<0.05). Three patients had no detectable blood flow on PDU. PDU of Achilles tendons does not seem to be strictly related to symptoms but rather to functionality and chronicity of tendinopathy as indicated by toe-raises testing, jumping capability, patient age and tendon thickening.
Vingt-cinq malades avec une tendinopathie chronique du tendon d'Achille ont été évalué d'une manière clinique et ultrasonographique. Une corrélation positive existait entre l'amplitude au doppler, l' épaisseur du tendon (r=0.63, p<0.001) et l'âge du malade (r=0.40, p<0.05). Une corrélation négative existait entre le doppler, un test functionnel et une article du 'Victorian Institute of Sport Assessment Achilles' questionnaire (VISA-A article 6: la capacité de saut) (r=−0.46, p<0.05). Trois malades n'avaient aucun courant sanguin détectable au doppler. L'amplitude ultrasonographique au niveau du tendon d'Achille ne paraissait pas en rapport avec les symptomes mais plutot avec la fonction et la chronicité de la tendinopathie comme indiqué par les différents test, l'age du patient et l'épaississement du tendon.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

