Horizontally transferred genes in plant-parasitic nematodes: a high-throughput genomic approach
- PMID: 12801413
- PMCID: PMC193618
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-6-r39
Horizontally transferred genes in plant-parasitic nematodes: a high-throughput genomic approach
Abstract
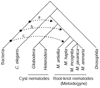
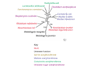
Background: Published accounts of horizontally acquired genes in plant-parasitic nematodes have not been the result of a specific search for gene transfer per se, but rather have emerged from characterization of individual genes. We present a method for a high-throughput genome screen for horizontally acquired genes, illustrated using expressed sequence tag (EST) data from three species of root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne species.
Results: Our approach identified the previously postulated horizontally transferred genes and revealed six new candidates. Screening was partially dependent on sequence quality, with more candidates identified from clustered sequences than from raw EST data. Computational and experimental methods verified the horizontal gene transfer candidates as bona fide nematode genes. Phylogenetic analysis implicated rhizobial ancestors as donors of horizontally acquired genes in Meloidogyne.
Conclusions: High-throughput genomic screening is an effective way to identify horizontal gene transfer candidates. Transferred genes that have undergone amelioration of nucleotide composition and codon bias have been identified using this approach. Analysis of these horizontally transferred gene candidates suggests a link between horizontally transferred genes in Meloidogyne and parasitism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactions between bacteria and plant-parasitic nematodes: now and then.Int J Parasitol. 2003 Sep 30;33(11):1269-76. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(03)00160-7. Int J Parasitol. 2003. PMID: 13678641 Review.
-
Analysis and functional classification of transcripts from the nematode Meloidogyne incognita.Genome Biol. 2003;4(4):R26. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-4-r26. Epub 2003 Mar 31. Genome Biol. 2003. PMID: 12702207 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence and genetic map of Meloidogyne hapla: A compact nematode genome for plant parasitism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 30;105(39):14802-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805946105. Epub 2008 Sep 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18809916 Free PMC article.
-
Role of horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of plant parasitism among nematodes.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;532:517-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-853-9_30. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19271205 Review.
-
Parasitology: Nematode debt to bacteria.Nature. 2010 Dec 2;468(7324):641-2. doi: 10.1038/468641a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 21124445 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Evolution, homology conservation, and identification of unique sequence signatures in GH19 family chitinases.J Mol Evol. 2010 May;70(5):466-78. doi: 10.1007/s00239-010-9345-z. Epub 2010 May 18. J Mol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20480157
-
Origin, evolution, and divergence of plant class C GH9 endoglucanases.BMC Evol Biol. 2018 May 30;18(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12862-018-1185-2. BMC Evol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29848310 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics Reveals Novel Target Genes towards Specific Control of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 13;11(11):1347. doi: 10.3390/genes11111347. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33202889 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired stress resilience through bacteria-to-nematode interdomain horizontal gene transfer.EMBO J. 2023 Dec 11;42(24):e114835. doi: 10.15252/embj.2023114835. Epub 2023 Nov 13. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37953666 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for horizontally transferred genes involved in the biosynthesis of vitamin B(1), B(5), and B(7) in Heterodera glycines.J Nematol. 2009 Dec;41(4):281-90. J Nematol. 2009. PMID: 22736827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boucher G, Lambshead PJD. Ecological biodiversity of marine nematodes in samples from temperate, tropical, and deep-sea regions. Conserv Biol. 1994;9:1594–1604.
-
- Bird DMcK, Koltai H. Plant parasitic nematodes: habitats, hormones, and horizontally-acquired genes. J Plant Growth Regul. 2000;19:183–194. - PubMed
-
- Blaxter ML, DeLey P, Garey J, Liu LX, Scheldeman P, Vierstraete A, Vanfletern J, Mackey LY, Dorris M, Frisse LM, et al. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature. 1998;392:71–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

