p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates cell death and p21-activated kinase mediates cell survival during chemotherapeutic drug-induced mitotic arrest
- PMID: 12802076
- PMCID: PMC165098
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0653
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates cell death and p21-activated kinase mediates cell survival during chemotherapeutic drug-induced mitotic arrest
Abstract
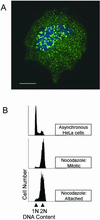
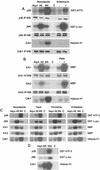
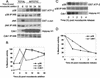
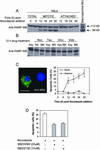
Activation of the mitotic checkpoint by chemotherapeutic drugs such as taxol causes mammalian cells to arrest in mitosis and then undergo apoptosis. However, the biochemical basis of chemotherapeutic drug-induced cell death is unclear. Herein, we provide new evidence that both cell survival and cell death-signaling pathways are concomitantly activated during mitotic arrest by microtubule-interfering drugs. Treatment of HeLa cells with chemotherapeutic drugs activated both p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and p21-activated kinase (PAK). p38 MAPK was necessary for chemotherapeutic drug-induced cell death because the p38 MAPK inhibitors SB203580 or SB202190 suppressed cell death. Dominant-active MKK6, a direct activator of p38 MAPK, also induced cell death by stimulating translocation of Bax from the cytosol to the mitochondria in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner. Dominant active PAK suppressed this MKK6-induced cell death. PAK seems to mediate cell survival by phosphorylating Bad, and inhibition of PAK in mitotically arrested cells reduced Bad phosphorylation and increased apoptosis. Our results suggest that therapeutic strategies that suppress PAK-mediated survival signals may improve the efficacy of current cancer chemotherapies by enhancing p38 MAPK-mediated cell death.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Opposite effects of Ha-Ras and Ki-Ras on radiation-induced apoptosis via differential activation of PI3K/Akt and Rac/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.Oncogene. 2004 Jan 8;23(1):9-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206982. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 14712206
-
The role of p38 MAPK and JNK in Arsenic trioxide-induced mitochondrial cell death in human cervical cancer cells.J Cell Physiol. 2008 Oct;217(1):23-33. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21470. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18412143
-
Phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase downstream of bax-caspase-3 pathway leads to cell death induced by high D-glucose in human endothelial cells.Diabetes. 2001 Jun;50(6):1472-81. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.6.1472. Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11375350
-
Stress Relief Techniques: p38 MAPK Determines the Balance of Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Pathways.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 2;11(10):1444. doi: 10.3390/biom11101444. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The p38 MAPK Signaling Activation in Colorectal Cancer upon Therapeutic Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 16;21(8):2773. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082773. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32316313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ROS production by mitochondria: function or dysfunction?Oncogene. 2024 Jan;43(5):295-303. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02907-z. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38081963 Review.
-
Ginaton injection alleviates cisplatin-induced renal interstitial fibrosis in rats via inhibition of apoptosis through regulation of the p38MAPK/TGF-β1 and p38MAPK/HIF-1α pathways.Biomed Rep. 2021 Apr;14(4):38. doi: 10.3892/br.2021.1414. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Biomed Rep. 2021. PMID: 33692901 Free PMC article.
-
Securin enhances the anti-cancer effects of 6-methoxy-3-(3',4',5'-trimethoxy-benzoyl)-1H-indole (BPR0L075) in human colorectal cancer cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036006. Epub 2012 Apr 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563433 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased glutathione levels potentiate the apoptotic efficacy of selenium: possible involvement of p38 and JNK MAPKs--in vitro studies.Mol Cell Biochem. 2008 Feb;309(1-2):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9639-7. Epub 2007 Nov 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17989939
-
OSU-DY7, a novel D-tyrosinol derivative, mediates cytotoxicity in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and Burkitt lymphoma through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.Br J Haematol. 2011 Jun;153(5):623-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08443.x. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Br J Haematol. 2011. PMID: 21470196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoshiba, K., Yasui, S., Hayashi, M., Tamaoki, J., and Nagai, A. (1999). Role of p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase in spontaneous apoptosis of human neutrophils. J. Immunol. 162, 1692–1700. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia, S., and Cerione, R.A. (1999). PAK to the future. Trends Cell Biol. 9, 350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia, S., Derijard, B., Davis, R.J., and Cerione, R.A. (1995). Cdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 27995–27998. - PubMed
-
- Burke, D. (2000). Complexity in the spindle checkpoint. Curr. Opin. Gen. Dev. 10, 26–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

