Lymphocyte subsets and T(h)1/T(h)2 immune responses in patients with adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus or oesophagogastric junction: relation to pTNM stage and clinical outcome
- PMID: 12802519
- PMCID: PMC11034314
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-003-0406-7
Lymphocyte subsets and T(h)1/T(h)2 immune responses in patients with adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus or oesophagogastric junction: relation to pTNM stage and clinical outcome
Abstract
Introduction: Recent studies have indicated that the cytokines produced by CD4(+) T helper type 1 (T(h)1) and type 2 (T(h)2) cells are critically important in antitumour immunity and perhaps clinical outcome. From this perspective, we investigated the immunocompetence of patients with previously untreated cancer of the oesophagus or oesophagogastric junction (OGJ) in relation to stage of disease and postoperative survival.
Methods: Blood samples were taken prior to surgery from 32 patients with adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus or OGJ. Ten healthy volunteers served as normal controls. T-cell and monocyte subpopulations were determined using flow cytometry. Monocyte as well as T(h)1- and T(h)2-lymphocyte cytokine levels were assessed in stimulated whole blood cultures.
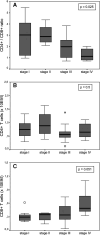
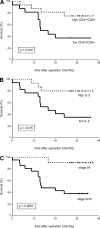
Results: Absolute T-cell and monocyte (subset) counts as well as monocyte cytokine levels were similar among patients and controls. Production of T(h)1-type cytokines was higher in patients than in controls (IFN-gamma, p=0.01; IL-2, p=0.05), whereas T(h)2-type cytokine levels were comparable (IL-4, p=0.5; IL-13, p=0.3). T-cell CD4(+)/CD8(+) ratios decreased as pTNM stage worsened (stage I/II vs stage III/IV, p=0.009). Of all measured immunological parameters, only IL-2 production significantly affected both overall survival ( p=0.015) and disease-free survival ( p=0.0062). High IL-2 levels corresponded with a favourable prognosis.
Conclusions: Patients awaiting surgery for adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus or oesophagogastric junction demonstrated a shift in the T(h)1/T(h)2 balance-in favour of T(h)1-compared with healthy volunteers. The ability of T cells to produce IL-2 was related to survival indicating a crucial role of T(h)1-type cells in antitumour immunosurveillance.
Figures
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

