The mechanism of action of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa-encoded type III cytotoxin, ExoU
- PMID: 12805211
- PMCID: PMC162142
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg290
The mechanism of action of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa-encoded type III cytotoxin, ExoU
Abstract
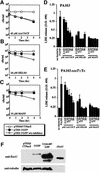
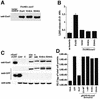
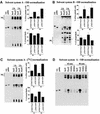
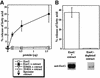
Pseudomonas aeruginosa delivers the toxin ExoU to eukaryotic cells via a type III secretion system. Intoxication with ExoU is associated with lung injury, bacterial dissemination and sepsis in animal model and human infections. To search for ExoU targets in a genetically tractable system, we used controlled expression of the toxin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ExoU was cytotoxic for yeast and caused a vacuolar fragmentation phenotype. Inhibitors of human calcium-independent (iPLA(2)) and cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) lipase activity reduce the cytotoxicity of ExoU. The catalytic domains of patatin, iPLA(2) and cPLA(2) align or are similar to ExoU sequences. Site-specific mutagenesis of predicted catalytic residues (ExoUS142A or ExoUD344A) eliminated toxicity. ExoU expression in yeast resulted in an accumulation of free palmitic acid, changes in the phospholipid profiles and reduction of radiolabeled neutral lipids. ExoUS142A and ExoUD344A expressed in yeast failed to release palmitic acid. Recombinant ExoU demonstrated lipase activity in vitro, but only in the presence of a yeast extract. From these data we conclude that ExoU is a lipase that requires activation or modification by eukaryotic factors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ExoU is a potent intracellular phospholipase.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Sep;53(5):1279-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04194.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15387809 Review.
-
In vivo phospholipase activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin ExoU and protection of mammalian cells with phospholipase A2 inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 17;278(42):41326-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302472200. Epub 2003 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12915403
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes acute lung injury via the catalytic activity of the patatin-like phospholipase domain of ExoU.Crit Care Med. 2004 Nov;32(11):2293-9. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000145588.79063.07. Crit Care Med. 2004. PMID: 15640644
-
Lysophospholipase A activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretory toxin ExoU.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Apr 2;316(2):323-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.02.050. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15020221
-
Association between Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion, antibiotic resistance, and clinical outcome: a review.Crit Care. 2014 Dec 13;18(6):668. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0668-9. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 25672496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal Regulation of Vibrio Exotoxins by HlyU and Other Transcriptional Regulators.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 22;12(9):544. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090544. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32842612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ExsE, a secreted regulator of type III secretion genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 31;102(22):8006-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503005102. Epub 2005 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15911752 Free PMC article.
-
ExoU Induces Lung Endothelial Cell Damage and Activates Pro-Inflammatory Caspase-1 during Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Feb 18;14(2):152. doi: 10.3390/toxins14020152. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35202178 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of phospholipase activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III cytotoxin, ExoU.J Bacteriol. 2005 Feb;187(3):1192-5. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.3.1192-1195.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15659695 Free PMC article.
-
Human- and plant-pathogenic Pseudomonas species produce bacteriocins exhibiting colicin M-like hydrolase activity towards peptidoglycan precursors.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jun;191(11):3657-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.01824-08. Epub 2009 Apr 3. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19346308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackermann E.J., Conde-Frieboes,K. and Dennis,E.A. (1995) Inhibition of macrophage Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 by bromoenol lactone and trifluoromethyl ketones. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 445–450. - PubMed
-
- Balsinde J. and Dennis,E.A. (1996) Distinct roles in signal transduction for each of the phospholipase A2 enzymes present in P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 6758–6765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

