Phospholipase Cdelta1 is required for skin stem cell lineage commitment
- PMID: 12805213
- PMCID: PMC162154
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg302
Phospholipase Cdelta1 is required for skin stem cell lineage commitment
Abstract
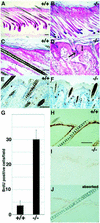
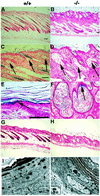
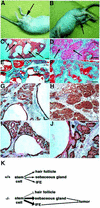
Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC) is a key enzyme in phosphoinositide turnover and is involved in a variety of physiological functions. Here we report that PLCdelta(1)-deficient mice undergo progressive hair loss in the first postnatal hair cycle. Epidermal hyperplasia was observed, and many hairs in the skin of PLCdelta(1)-deficient mice failed to penetrate the epidermis and became zigzagged owing to occlusion of the hair canal. Two major downstream signals of PLC, calcium elevation and protein kinase C activation, were impaired in the keratinocytes and skin of PLCdelta(1)-deficient mice. In addition, many cysts that had remarkable similarities to interfollicular epidermis, as well as hyperplasia of sebaceous glands, were observed. Furthermore, PLCdelta(1)-deficient mice developed spontaneous skin tumors that had characteristics of both interfollicular epidermis and sebaceous glands. From these results, we conclude that PLCdelta(1) is required for skin stem cell lineage commitment.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Lgr6 marks stem cells in the hair follicle that generate all cell lineages of the skin.Science. 2010 Mar 12;327(5971):1385-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1184733. Science. 2010. PMID: 20223988
-
Hair follicle defects and squamous cell carcinoma formation in Smad4 conditional knockout mouse skin.Oncogene. 2006 Jan 12;25(2):207-17. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209029. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16170355
-
Human skin stem cells and the ageing process.Exp Gerontol. 2008 Nov;43(11):986-97. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2008.09.001. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Exp Gerontol. 2008. PMID: 18809487 Review.
-
Distinct stem cell populations regenerate the follicle and interfollicular epidermis.Dev Cell. 2005 Dec;9(6):855-61. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.11.003. Dev Cell. 2005. PMID: 16326396
-
Epidermal stem cells: practical perspectives and potential uses.Br J Dermatol. 2009 Aug;161(2):228-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09250.x. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Br J Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19548960 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipase Cdelta3 regulates RhoA/Rho kinase signaling and neurite outgrowth.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 11;286(10):8459-8471. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.171223. Epub 2010 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21187285 Free PMC article.
-
Skin Diseases in Laboratory Mice: Approaches to Drug Target Identification and Efficacy Screening.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1438:199-224. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3661-8_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27150092 Free PMC article.
-
'One medicine---one pathology': are veterinary and human pathology prepared?Lab Invest. 2008 Jan;88(1):18-26. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700695. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Lab Invest. 2008. PMID: 18040269 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase Cδ1 regulates p38 MAPK activity and skin barrier integrity.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Jun;24(6):1079-1090. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.56. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28430185 Free PMC article.
-
Osmotically evoked PLCδ1-dependent translocation of ΔN-TRPV1 channels in rat supraoptic neurons.iScience. 2023 Feb 20;26(3):106258. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106258. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36926650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beg A.A. and Baltimore,D. (1996) An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science, 274, 782–784. - PubMed
-
- Berridge M.J. and Irvine,R.F. (1984) Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature, 312, 315–321. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay N., Mithal,A. and Brown,E.M. (1996) The calcium-sensing receptor: a window into the physiology and pathophysiology of mineral ion metabolism. Endocr. Rev., 17, 289–307. - PubMed
-
- Dolmetsch R.E., Lewis,R.S., Goodnow,C.C. and Healy,J.I. (1997) Differential activation of transcription factors induced by Ca2+ response amplitude and duration. Nature, 386, 855–858. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

