Noggin overexpression inhibits eyelid opening by altering epidermal apoptosis and differentiation
- PMID: 12805214
- PMCID: PMC162143
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg291
Noggin overexpression inhibits eyelid opening by altering epidermal apoptosis and differentiation
Abstract
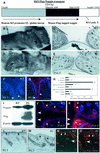
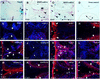
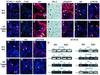
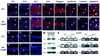
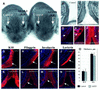
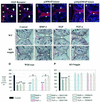
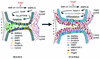
Contact of developing sensory organs with the external environment is established via the formation of openings in the skin. During eye development, eyelids first grow, fuse and finally reopen, thus providing access for visual information to the retina. Here, we show that eyelid opening is strongly inhibited in transgenic mice overexpressing the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonist noggin from the keratin 5 (K5) promoter in the epidermis. In wild-type mice, enhanced expression of the kinase-inactive form of BMPR-IB mediated by an adenovirus vector also inhibits eyelid opening. Noggin overexpression leads to reduction of apoptosis and retardation of cell differentiation in the eyelid epithelium, which is associated with downregulation of expression of the apoptotic receptors (Fas, p55 kDa TNFR), Id3 protein and keratinocyte differentiation markers (loricrin, involucrin). BMP-4, but not EGF or TGF-alpha, accelerates opening of the eyelid explants isolated from K5-Noggin transgenic mice when cultured ex vivo. These data suggest that the BMP signaling pathway plays an important role in regulation of genetic programs of eyelid opening and skin remodeling during the final steps of eye morphogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling controls hair pigmentation by means of cross-talk with the melanocortin receptor-1 pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jan 4;102(1):93-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408455102. Epub 2004 Dec 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15618398 Free PMC article.
-
Bmp signaling is required for development of primary lens fiber cells.Development. 2002 Aug;129(15):3727-37. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.15.3727. Development. 2002. PMID: 12117821
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 is expressed by, and acts upon, mature epithelial cells in the colon.Gastroenterology. 2004 Jan;126(1):111-21. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.10.067. Gastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 14699493
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
Epidermal differentiation and keratin gene expression.J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:197-208. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.28. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993. PMID: 7511614 Review.
Cited by
-
Delayed Formation of Neonatal Reflexes and of Locomotor Skills Is Associated with Poor Maternal Behavior in OXYS Rats Prone to Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 12;10(11):2910. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112910. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36428477 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental and functional significance of the CSF-1 proteoglycan chondroitin sulfate chain.Blood. 2006 Jan 15;107(2):786-95. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1822. Epub 2005 Oct 6. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16210339 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed Cell Death Not as Sledgehammer but as Chisel: Apoptosis in Normal and Abnormal Craniofacial Patterning and Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 8;9:717404. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.717404. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34692678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The aging of the 2000 and 2011 Hallmarks of Cancer reviews: a critique.J Biosci. 2013 Sep;38(3):651-63. doi: 10.1007/s12038-013-9335-6. J Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23938395 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21 is an important downstream component of BMP signalling in epidermal keratinocytes.J Cell Sci. 2011 Oct 15;124(Pt 20):3399-404. doi: 10.1242/jcs.086710. Epub 2011 Oct 7. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21984808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki H., Fujii,M., Imamura,T., Yagi,K., Takehara,K., Kato,M. and Miyazono K. (2001) Synergistic effects of different bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors on alkaline phosphatase induction. J. Cell Sci., 114, 1483–1489. - PubMed
-
- Blessing M., Nanney,L., King,L., Jones,C. and Hogan,B.L. (1993) Transgenic mice as a model to study the role of TGF-β-related molecules in hair follicles. Genes Dev., 7, 204–215. - PubMed
-
- Blessing M., Schirmacher,P. and Kaiser,S. (1996) Overexpression of bone morphogenetic protein-6 in the epidermis of transgenic mice: inhibition or stimulation of proliferation depending on the pattern of transgene expression and formation of psoriatic lesions. J. Cell Biol., 135, 227–239. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Botchkarev V.A. (2003) Bone morphogenetic proteins and their antagonists in skin and hair follicle biology. J. Invest. Dermatol., 120, 36–47. - PubMed
-
- Botchkarev V., Botchkareva,N., Roth,W., Nakamura,M., McMahon,J.A., McMahon,A. and Paus,R. (1999) Noggin is a mesenchymally-derived stimulator of hair follicle induction. Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 158–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

