GAP43 stimulates inositol trisphosphate-mediated calcium release in response to hypotonicity
- PMID: 12805215
- PMCID: PMC162146
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg294
GAP43 stimulates inositol trisphosphate-mediated calcium release in response to hypotonicity
Abstract
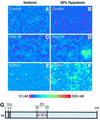
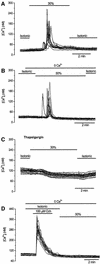
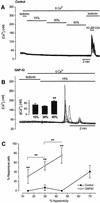
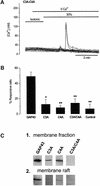
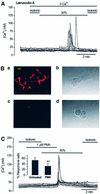
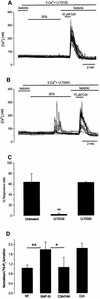
The identification of osmo/mechanosensory proteins in mammalian sensory neurons is still elusive. We have used an expression cloning approach to screen a human dorsal root ganglion cDNA library to look for proteins that respond to hypotonicity by raising the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)). We report the unexpected identification of GAP43 (also known as neuromodulin or B50), a membrane-anchored neuronal protein implicated in axonal growth and synaptic plasticity, as an osmosensory protein that augments [Ca(2+)](i) in response to hypotonicity. Palmitoylation of GAP43 plays an important role in the protein osmosensitivity. Depletion of intracellular stores or inhibition of phospholipase C (PLC) activity abrogates hypotonicity-evoked, GAP43-mediated [Ca(2+)](i) elevations. Notably, hypotonicity promoted the selective association of GAP43 with the PLC-delta(1) isoform, and a concomitant increase in inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP(3)) formation. Collectively, these findings indicate that hypo-osmotic activation of GAP43 induces Ca(2+) release from IP(3)-sensitive intracellular stores. The osmosensitivity of GAP43 furnishes a mechanistic framework that links axon elongation with phospho inositide metabolism, spontaneous triggering of cytosolic Ca(2+) transients and the regulation of actin dynamics and motility at the growth cone in response to temporal and local mechanical forces.
Figures

References
-
- Arni S., Keilbaugh,S.A., Ostermeyer,A.G. and Brown,D.A. (1998) Association of GAP-43 with detergent-resistant membranes requires two palmitoylated cysteine residues. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 28478–28485. - PubMed
-
- Bomze H.M., Bulsara,K.R., Iskandar,B.J., Caroni,P. and Pate Skene,J.H. (2001) Spinal axon regeneration evoked by replacing two growth cone proteins in adult neurons. Nature Neurosci., 4, 38–43. - PubMed
-
- Bourque C.W. and Oliet,S.H.R. (1997) Osmoreceptors in the central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 59, 601–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

