NSD1 is essential for early post-implantation development and has a catalytically active SET domain
- PMID: 12805229
- PMCID: PMC162140
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg288
NSD1 is essential for early post-implantation development and has a catalytically active SET domain
Abstract
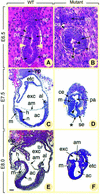
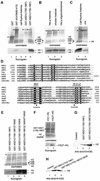
The nuclear receptor-binding SET domain-containing protein (NSD1) belongs to an emerging family of proteins, which have all been implicated in human malignancy. To gain insight into the biological functions of NSD1, we have generated NSD1-deficient mice by gene disruption. Homozygous mutant NSD1 embryos, which initiate mesoderm formation, display a high incidence of apoptosis and fail to complete gastrulation, indicating that NSD1 is a developmental regulatory protein that exerts function(s) essential for early post-implantation development. We have also examined the enzymatic potential of NSD1 and found that its SET domain possesses intrinsic histone methyltransferase activity with specificity for Lys36 of histone H3 (H3-K36) and Lys20 of histone H4 (H4-K20).
Figures



References
-
- Aasland R., Gibson,T.J. and Stewart,A.F. (1995) The PHD finger: implications for chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci., 20, 56–59. - PubMed
-
- Angrand P.O., Apiou,F., Stewart,A.F., Dutrillaux,B., Losson,R. and Chambon,P. (2001) NSD3, a new SET domain-containing gene, maps to 8p12 and is amplified in human breast cancer cell lines. Genomics, 74, 79–88. - PubMed
-
- Beisel C., Imhof,A., Greene,J., Kremmer,E. and Sauer,F. (2002) Histone methylation by the Drosophila epigenetic regulator Ash1. Nature, 419, 857–862. - PubMed
-
- Chesi M., Nardini,E., Lim,R.S., Smith,K.D., Kuehl,W.M. and Bergsagel,P.L. (1998) The t(4;14) translocation in myeloma dysregulates both FGFR3 and a novel gene, MMSET, resulting in IgH/MMSET hybrid transcripts. Blood, 92, 3025–3034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

