Refined annotation of the Arabidopsis genome by complete expressed sequence tag mapping
- PMID: 12805580
- PMCID: PMC166990
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.102.018101
Refined annotation of the Arabidopsis genome by complete expressed sequence tag mapping
Abstract
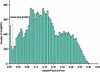
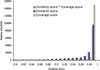
Expressed sequence tags (ESTs) currently encompass more entries in the public databases than any other form of sequence data. Thus, EST data sets provide a vast resource for gene identification and expression profiling. We have mapped the complete set of 176,915 publicly available Arabidopsis EST sequences onto the Arabidopsis genome using GeneSeqer, a spliced alignment program incorporating sequence similarity and splice site scoring. About 96% of the available ESTs could be properly aligned with a genomic locus, with the remaining ESTs deriving from organelle genomes and non-Arabidopsis sources or displaying insufficient sequence quality for alignment. The mapping provides verified sets of EST clusters for evaluation of EST clustering programs. Analysis of the spliced alignments suggests corrections to current gene structure annotation and provides examples of alternative and non-canonical pre-mRNA splicing. All results of this study were parsed into a database and are accessible via a flexible Web interface at http://www.plantgdb.org/AtGDB/.
Figures





References
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796–815 - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C (1994) Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 2: 28–36 - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Gribskov M (1998) Combining evidence using p-values: application to sequence homology searches. Bioinformatics 14: 48–54 - PubMed
-
- Berget SM (1995) Exon recognition in vertebrate splicing. J Biol Chem 270: 2411–2414 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

