Enhancer trapping reveals widespread circadian clock transcriptional control in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12805593
- PMCID: PMC167003
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.021006
Enhancer trapping reveals widespread circadian clock transcriptional control in Arabidopsis
Abstract
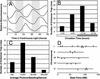
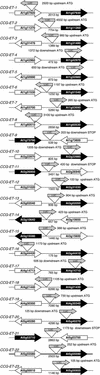
The circadian clock synchronizes the internal biology of an organism with the environment and has been shown to be widespread among organisms. Microarray experiments have shown that the circadian clock regulates mRNA abundance of about 10% of the transcriptome in plants, invertebrates, and mammals. In contrast, the circadian clock regulates the transcription of the virtually all cyanobacterial genes. To determine the extent to which the circadian clock controls transcription in Arabidopsis, we used in vivo enhancer trapping. We found that 36% of our enhancer trap lines display circadian-regulated transcription, which is much higher than estimates of circadian regulation based on analysis of steady-state mRNA abundance. Individual lines identified by enhancer trapping exhibit peak transcription rates at circadian phases spanning the complete circadian cycle. Flanking genomic sequence was identified for 23 enhancer trap lines to identify clock-controlled genes (CCG-ETs). Promoter analysis of CCG-ETs failed to predict new circadian clock response elements (CCREs), although previously defined CCREs, the CCA1-binding site, and the evening element were identified. However, many CCGs lack either the CCA1-binding site or the evening element; therefore, the presence of these CCREs is insufficient to confer circadian regulation, and it is clear that additional elements play critical roles.
Figures

References
-
- Akhtar RA, Reddy AB, Maywood ES, Clayton JD, King VM, Smith AG, Gant TW, Hastings MH, Kyriacou CP (2002) Circadian cycling of the mouse liver transcriptome, as revealed by cDNA microarray, is driven by the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Curr Biol 12: 540–550 - PubMed
-
- Alabadí D, Oyama T, Yanovsky MJ, Harmon FG, Más P, Kay SA (2001) Reciprocal regulation between TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 293: 880–883 - PubMed
-
- Alabadí D, Yanovsky MJ, Más P, Harmer SL, Kay SA (2002) Critical role for CCA1 and LHY in maintaining circadian rhythmicity in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 12: 757–761 - PubMed
-
- Aoki S, Kondo T, Ishiura M (2002) A promoter-trap vector for clock-controlled genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J Microbiol Methods 49: 265–274 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

