Induction of interleukin-12 production in mouse macrophages by berberine, a benzodioxoloquinolizine alkaloid, deviates CD4+ T cells from a Th2 to a Th1 response
- PMID: 12807487
- PMCID: PMC1782983
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01673.x
Induction of interleukin-12 production in mouse macrophages by berberine, a benzodioxoloquinolizine alkaloid, deviates CD4+ T cells from a Th2 to a Th1 response
Abstract
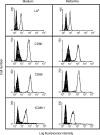
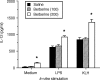
In this study we investigated whether berberine-mediated induction of interleukin-12 (IL-12) production in antigen-presenting cells could regulate a cytokine profile of antigen-primed CD4+ T helper (Th) cells. Pretreatment with berberine induced IL-12 production in both macrophages and dendritic cells, and significantly increased the levels of IL-12 production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages and in CD40 ligand-stimulated dendritic cells. Importantly, berberine pretreatment of macrophages increased their ability to induce interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and reduced their ability to induce IL-4 in antigen-primed CD4+ T cells. Berberine did not influence the macrophage cell surface expression of the class II major histocompatibility complex molecule, the co-stimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86, and intracellular adhesion molecule-1. Addition of neutralizing anti-IL-12p40 monoclonal antibody to cultures of berberine-pretreated macrophages and CD4+ T cells restored IL-4 production in antigen-primed CD4+ T cells. The in vivo administration of berberine resulted in the enhanced induction of IL-12 production by macrophages when stimulated in vitro with lipopolysaccharide or heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes, leading to the inhibition of the Th type 2 cytokine profile (decreased IL-4 and increased IFN-gamma production) in antigen-primed CD4+ T cells. These findings may point to a possible therapeutic use of berberine or medicinal plants containing berberine in the Th type 2 cell-mediated immune diseases such as allergic diseases.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of interleukin-12 production by auranofin, an anti-rheumatic gold compound, deviates CD4(+) T cells from the Th1 to the Th2 pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct;134(3):571-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704298. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11588111 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin inhibits Th1 cytokine profile in CD4+ T cells by suppressing interleukin-12 production in macrophages.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Sep;128(2):380-4. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702803. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10510448 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid-mediated inhibition of interleukin-12 production in mouse macrophages suppresses Th1 cytokine profile in CD4(+) T cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jun;130(3):581-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703345. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10821786 Free PMC article.
-
The two faces of IL-6 on Th1/Th2 differentiation.Mol Immunol. 2002 Dec;39(9):531-6. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00210-9. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12431386 Review.
-
Co-stimulation and modulation of the ensuing immune response.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002 Sep 10;87(3-4):123-30. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(02)00043-0. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002. PMID: 12072226 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the Immunomodulatory effect of Berberis vulgaris on core-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Aug 30;16(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1327-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27577059 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence Supporting a Phased Immuno-physiological Approach to COVID-19 From Prevention Through Recovery.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2020;19(Suppl 1):8-35. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2020. PMID: 32425712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro biological assessment of Berberis vulgaris and its active constituent, berberine: antioxidants, anti-acetylcholinesterase, anti-diabetic and anticancer effects.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Sep 5;13:218. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-218. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 24007270 Free PMC article.
-
The changes in the T helper 1 (Th1) and T helper 2 (Th2) cytokine balance during HIV-1 infection are indicative of an allergic response to viral proteins that may be reversed by Th2 cytokine inhibitors and immune response modifiers--a review and hypothesis.Virus Genes. 2004 Jan;28(1):5-18. doi: 10.1023/B:VIRU.0000012260.32578.72. Virus Genes. 2004. PMID: 14739648 Review.
-
Berberine inhibits acute radiation intestinal syndrome in human with abdomen radiotherapy.Med Oncol. 2010 Sep;27(3):919-25. doi: 10.1007/s12032-009-9307-8. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Med Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19757213 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. Th1 and Th2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;9:145–73. - PubMed
-
- Chtanova T, Mackay CR. T cell effector subsets: extending the Th1/Th2 paradigm. Adv Immunol. 2001;78:233–66. - PubMed
-
- Singh VK, Mehrotra S, Agarwal SS. The paradigm of Th1 and Th2 cytokines: its relevance to autoimmunity and allergy. Immunol Res. 1999;20:147–61. - PubMed
-
- Spellberg B, Edwards JE., Jr Type 1/type 2 immunity in infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:76–102. - PubMed
-
- Boothby M, Mora AL, Aronica MA, Youn J, Sheller JR, Goenka S, Stephenson L. IL-4 signaling, gene transcription regulation, and the control of effector T cells. Immunol Res. 2001;23:179–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

