Effects of nimesulide on kainate-induced in vitro oxidative damage in rat brain homogenates
- PMID: 12807536
- PMCID: PMC165434
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-3-7
Effects of nimesulide on kainate-induced in vitro oxidative damage in rat brain homogenates
Abstract
Background: The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor nimesulide is able to reduce kainate-induced oxidative stress in vivo. Here we investigate if this effect is mediated by the direct antioxidant properties of nimesulide using a well-characterized in vitro model of kainate toxicity.
Results: Exposure of rat brain homogenates to kainate (12 mM) caused a significant (p < 0.01) increase in the concentrations of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-alkenals and a significant (p < 0.01) decrease in sulfhydryl levels. High concentrations of nimesulide (0.6-1.6 mM) reduced the extent of lipid peroxidation and the decline in both total and non-protein sulfhydryl levels induced by kainate in a concentration-dependent manner.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the neuroprotective effects of nimesulide against kainate-induced oxidative stress in vivo are not mediated through its direct free radical scavenging ability because the concentrations at which nimesulide is able to reduce in vitro kainate excitotoxicity are excessively higher than those attained in plasma after therapeutic doses.
Figures
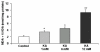
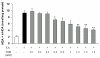
Similar articles
-
Nimesulide limits kainate-induced oxidative damage in the rat hippocampus.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar 3;390(3):295-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00908-5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10708736
-
Differential effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on intracerebroventricular colchicine-induced dysfunction and oxidative stress in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Dec 3;551(1-3):58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.08.076. Epub 2006 Sep 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17027965
-
Cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats: possible antioxidant mechanisms.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;21(3):297-306. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2007.00485.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17521299
-
Nimesulide prevents oxidative stress damage following transient forebrain ischemia in the rat hippocampus.Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 2004;115-116:49-62. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 17564305
-
Neurochemical consequences of kainate-induced toxicity in brain: involvement of arachidonic acid release and prevention of toxicity by phospholipase A(2) inhibitors.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001 Dec;38(1-2):61-78. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(01)00214-5. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11750927 Review.
Cited by
-
Kainic acid-mediated excitotoxicity as a model for neurodegeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2005;31(1-3):3-16. doi: 10.1385/MN:31:1-3:003. Mol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 15953808 Review.
References
-
- Davis R, Brogden RN. Nimesulide. An update of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1994;48:431–454. - PubMed
-
- Rabasseda X. Nimesulide: a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor antiinflammatory dru. Drugs Today. 1996;32:1–23.
-
- Rossoni G, Berti F, Buschi LM, Della Bella D. New data concerning the anaphylactic and antihistaminic activity of nimesulid. Drugs. 1993;46:22–28. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira SH. The role of interleukins and nitric oxide in the mediation of inflammatory pain and its control by peripheral analgesic. Drugs. 1993;46:1–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

