Golgi localization of Syne-1
- PMID: 12808039
- PMCID: PMC194889
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-07-0446
Golgi localization of Syne-1
Abstract
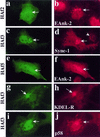
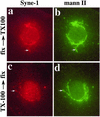
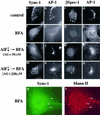
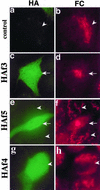
We have previously identified a Golgi-localized spectrin isoform by using an antibody to the beta-subunit of erythrocyte spectrin. In this study, we show that a screen of a lambdagt11 expression library resulted in the isolation of an approximately 5-kb partial cDNA from a Madin-Darby bovine kidney (MDBK) cell line, which encoded a polypeptide of 1697 amino acids with low, but detectable, sequence homology to spectrin (37%). A blast search revealed that this clone overlaps with the 5' end of a recently identified spectrin family member Syne-1B/Nesprin-1beta, an alternately transcribed gene with muscle-specific forms that bind acetylcholine receptor and associate with the nuclear envelope. By comparing the sequence of the MDBK clone with sequence data from the human genome database, we have determined that this cDNA represents a central portion of a very large gene ( approximately 500 kb), encoding an approximately 25-kb transcript that we refer to as Syne-1. Syne-1 encodes a large polypeptide (8406 amino acids) with multiple spectrin repeats and a region at its amino terminus with high homology to the actin binding domains of conventional spectrins. Golgi localization for this spectrin-like protein was demonstrated by expression of epitope-tagged fragments in MDBK and COS cells, identifying two distinct Golgi binding sites, and by immunofluorescence microscopy by using several different antibody preparations. One of the Golgi binding domains on Syne-1 acts as a dominant negative inhibitor that alters the structure of the Golgi complex, which collapses into a condensed structure near the centrosome in transfected epithelial cells. We conclude that the Syne-1 gene is expressed in a variety of forms that are multifunctional and are capable of functioning at both the Golgi and the nuclear envelope, perhaps linking the two organelles during muscle differentiation.
Figures





References
-
- Apel, E.D., Lewis, R.M., Grady, M., and Sanes, J.R. (2000). Syne-1, a dystrophin- and klarsicht-related protein associated with synaptic nuclei at the neuromuscular junction. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 31986-31995. - PubMed
-
- Babiá, T., Ayala, I., Valderrama, F., Mato, E., Bosch, M., Santarén, J.F., Renau-Piqueras, J., Kok, J.W., Thomson, T.M., and Egea, G. (1999). N-Ras induces alterations in Golgi complex architecture and in constitutive protein transport. J. Cell Sci. 112, 477-489. - PubMed
-
- Beck, K., Buchanan, J.A., and Nelson, W.J. (1997). Golgi membrane skeleton: identification, localization and oligomerization of a 195 kD ankyrin isoform associated with the Golgi complex. J. Cell Sci. 110, 1239-1249. - PubMed
-
- Beck, K., and Nelson, W.J. (1998). A spectrin membrane skeleton of the Golgi complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1404, 153-160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

